Structural, Genetic, and Serological Elucidation of Streptococcus pneumoniae Serogroup 24 Serotypes: Discovery of a New Serotype, 24C, with a Variable Capsule Structure
- PMID: 33883183
- PMCID: PMC8218768
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00540-21
Structural, Genetic, and Serological Elucidation of Streptococcus pneumoniae Serogroup 24 Serotypes: Discovery of a New Serotype, 24C, with a Variable Capsule Structure
Abstract
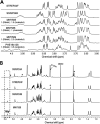
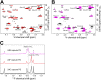
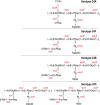
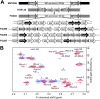
Pneumococcal capsules are important in pneumococcal pathogenesis and vaccine development. Although conjugate vaccines have brought about a significant reduction in invasive pneumococcal disease (IPD) caused by vaccine serotypes, the relative serotype prevalence has shifted with the dramatic emergence of serotype 24F in some countries. Here, we describe 14 isolates (13 IPD and 1 non-IPD) expressing a new capsule type, 24C, which resembles 24F but has a novel serological profile. We also describe the antigenic, biochemical, and genetic basis of 24F and 24C and the related serotypes 24A and 24B. Structural studies show that 24B, 24C, and 24F have identical polysaccharide backbones [β-Ribf-(1→4)-α-Rhap-(1→3)-β-GlcpNAc-(1→4)-β-Rhap-(1→4)-β-Glcp] but with different side chains, as follows: 24F has arabinitol-phosphate and 24B has ribitol-phosphate. 24C has a mixture of 24F and 24B repeating units, with the ratio of ribitol to arabinitol being strain dependent. In contrast, the 24A capsule has a backbone without β-Ribf but with arabinitol-phosphate and phosphocholine side chains. These structures indicate that factor-sera 24d and 24e recognize arabinitol and ribitol, respectively, which explains the serology of serogroup 24, including those of 24C. The structures can be genetically described by the bispecificity of wcxG, which is capable of transferring arabinitol or ribitol when arabinitol is limiting. Arabinitol is likely not produced in 24B but is produced in reduced amounts in 24C due to various mutations in abpA or abpB genes. Our findings demonstrate how pneumococci modulate their capsule structure and immunologic properties with small genetic changes, thereby evading host immune responses. Our findings also suggest a potential for new capsule types within serogroup 24.
Keywords: Streptococcus pneumoniae; capsule polysaccharide; genetic heterogeneity; serogroup; vaccine.
Figures

References
-
- Siber GR, Thompson C, Reid GR, Almeido-Hill J, Zacher B, Wolff M, Santosham M. 1992. Evaluation of bacterial polysaccharide immune globulin for the treatment or prevention of Haemophilus influenzae type b and pneumococcal disease. J Infect Dis 165:S129–S133. 10.1093/infdis/165-supplement_1-s129. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Andrews NJ, Waight PA, Burbidge P, Pearce E, Roalfe L, Zancolli M, Slack M, Ladhani SN, Miller E, Goldblatt D. 2014. Serotype-specific effectiveness and correlates of protection for the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine: a postlicensure indirect cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis 14:839–846. 10.1016/S1473-3099(14)70822-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Croucher NJ, Harris SR, Fraser C, Quail MA, Burton J, van der Linden M, McGee L, von Gottberg A, Song JH, Ko KS, Pichon B, Baker S, Parry CM, Lambertsen LM, Shahinas D, Pillai DR, Mitchell TJ, Dougan G, Tomasz A, Klugman KP, Parkhill J, Hanage WP, Bentley SD. 2011. Rapid pneumococcal evolution in response to clinical interventions. Science 331:430–434. 10.1126/science.1198545. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

