Sphingosine kinase 1 regulates lysyl oxidase through STAT3 in hyperoxia-mediated neonatal lung injury
- PMID: 33883249
- PMCID: PMC9115769
- DOI: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2020-216469
Sphingosine kinase 1 regulates lysyl oxidase through STAT3 in hyperoxia-mediated neonatal lung injury
Abstract
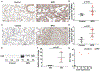
Introduction: Neonatal lung injury as a consequence of hyperoxia (HO) therapy and ventilator care contribute to the development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD). Increased expression and activity of lysyl oxidase (LOX), a key enzyme that cross-links collagen, was associated with increased sphingosine kinase 1 (SPHK1) in human BPD. We, therefore, examined closely the link between LOX and SPHK1 in BPD.
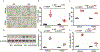
Method: The enzyme expression of SPHK1 and LOX were assessed in lung tissues of human BPD using immunohistochemistry and quantified (Halo). In vivo studies were based on Sphk1-/- and matched wild type (WT) neonatal mice exposed to HO while treated with PF543, an inhibitor of SPHK1. In vitro mechanistic studies used human lung microvascular endothelial cells (HLMVECs).
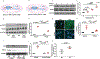
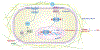
Results: Both SPHK1 and LOX expressions were increased in lungs of patients with BPD. Tracheal aspirates from patients with BPD had increased LOX, correlating with sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) levels. HO-induced increase of LOX in lungs were attenuated in both Sphk1-/- and PF543-treated WT mice, accompanied by reduced collagen staining (sirius red). PF543 reduced LOX activity in both bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and supernatant of HLMVECs following HO. In silico analysis revealed STAT3 as a potential transcriptional regulator of LOX. In HLMVECs, following HO, ChIP assay confirmed increased STAT3 binding to LOX promoter. SPHK1 inhibition reduced phosphorylation of STAT3. Antibody to S1P and siRNA against SPNS2, S1P receptor 1 (S1P1) and STAT3 reduced LOX expression.
Conclusion: HO-induced SPHK1/S1P signalling axis plays a critical role in transcriptional regulation of LOX expression via SPNS2, S1P1 and STAT3 in lung endothelium.
Keywords: long term oxygen therapy (LTOT); oxidative stress; paediatric interstitial lung disease; paediatric lung disaese.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
