Role of bacterial RNA polymerase gate opening dynamics in DNA loading and antibiotics inhibition elucidated by quasi-Markov State Model
- PMID: 33883282
- PMCID: PMC8092612
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2024324118
Role of bacterial RNA polymerase gate opening dynamics in DNA loading and antibiotics inhibition elucidated by quasi-Markov State Model
Abstract
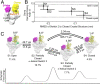
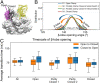
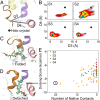
To initiate transcription, the holoenzyme (RNA polymerase [RNAP] in complex with σ factor) loads the promoter DNA via the flexible loading gate created by the clamp and β-lobe, yet their roles in DNA loading have not been characterized. We used a quasi-Markov State Model (qMSM) built from extensive molecular dynamics simulations to elucidate the dynamics of Thermus aquaticus holoenzyme's gate opening. We showed that during gate opening, β-lobe oscillates four orders of magnitude faster than the clamp, whose opening depends on the Switch 2's structure. Myxopyronin, an antibiotic that binds to Switch 2, was shown to undergo a conformational selection mechanism to inhibit clamp opening. Importantly, we reveal a critical but undiscovered role of β-lobe, whose opening is sufficient for DNA loading even when the clamp is partially closed. These findings open the opportunity for the development of antibiotics targeting β-lobe of RNAP. Finally, we have shown that our qMSMs, which encode non-Markovian dynamics based on the generalized master equation formalism, hold great potential to be widely applied to study biomolecular dynamics.
Keywords: Markov State Model; bacterial RNA polymerase; transcription initiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Site-specific aptamer inhibitors of Thermus RNA polymerase.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Jan 1;495(1):110-115. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.10.151. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29097207
-
Distinct functions of regions 1.1 and 1.2 of RNA polymerase σ subunits from Escherichia coli and Thermus aquaticus in transcription initiation.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jul 6;287(28):23779-89. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.363242. Epub 2012 May 17. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22605342 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of a bacterial RNA polymerase holoenzyme open promoter complex.Elife. 2015 Sep 8;4:e08504. doi: 10.7554/eLife.08504. Elife. 2015. PMID: 26349032 Free PMC article.
-
How to switch the motor on: RNA polymerase initiation steps at the single-molecule level.Protein Sci. 2017 Jul;26(7):1303-1313. doi: 10.1002/pro.3183. Epub 2017 May 12. Protein Sci. 2017. PMID: 28470684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial RNA polymerases: the wholo story.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2003 Feb;13(1):31-9. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(02)00005-2. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2003. PMID: 12581657 Review.
Cited by
-
Automated Path Searching Reveals the Mechanism of Hydrolysis Enhancement by T4 Lysozyme Mutants.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 23;23(23):14628. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314628. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36498954 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative generalized master equation: A method to study long-timescale biomolecular dynamics via the integrals of memory kernels.J Chem Phys. 2023 Oct 7;159(13):134106. doi: 10.1063/5.0167287. J Chem Phys. 2023. PMID: 37787134 Free PMC article.
-
Early intermediates in bacterial RNA polymerase promoter melting visualized by time-resolved cryo-electron microscopy.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024 Nov;31(11):1778-1788. doi: 10.1038/s41594-024-01349-9. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38951624
-
Markov State Models to Study the Functional Dynamics of Proteins in the Wake of Machine Learning.JACS Au. 2021 Aug 4;1(9):1330-1341. doi: 10.1021/jacsau.1c00254. eCollection 2021 Sep 27. JACS Au. 2021. PMID: 34604842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Bacterial RNA Polymerase: Harnessing Simulations and Machine Learning to Design Inhibitors for Drug-Resistant Pathogens.Biochemistry. 2025 Mar 18;64(6):1169-1179. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.4c00751. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Biochemistry. 2025. PMID: 40014017 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

