Early Diagnosis of HIV-1 and HIV-2 Using Cobas HIV-1/HIV-2 Qualitative Test: A Novel Qualitative Nucleic Acid Amplification Test for Plasma, Serum, and Dried Blood Spot Specimens
- PMID: 33883470
- PMCID: PMC8263138
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000002713
Early Diagnosis of HIV-1 and HIV-2 Using Cobas HIV-1/HIV-2 Qualitative Test: A Novel Qualitative Nucleic Acid Amplification Test for Plasma, Serum, and Dried Blood Spot Specimens
Abstract
Background: Nucleic acid amplification tests (NATs) minimize the time from HIV infection to diagnosis, reducing transmission during acute HIV. NATs are especially useful for diagnosing HIV in children younger than 18 months and discriminating between HIV-1 and HIV-2.
Methods: We evaluated the performance of the cobas HIV-1/HIV-2 qualitative (cobas HIV-1/2 Qual) test for use on cobas 6800/8800 Systems. The results of adult plasma and serum samples and pediatric dried blood spots were compared with those of the recomLine HIV-1 & HIV-2 Immunoglobulin G serological test and COBAS AmpliPrep/COBAS TaqMan HIV-1 qualitative test, v2.0. Genotype inclusivity and limits of detection were determined, and sensitivity on seroconversion panels was compared with that in the Bio-Rad Geenius HIV 1/2 Confirmatory Assay, Abbott ARCHITECT HIV Ag/Ab Combo serological test, and cobas TaqScreen MPX, v2.0.
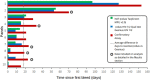
Results: Concordance of cobas HIV-1/2 Qual test with the comparator serological test and COBAS AmpliPrep/COBAS TaqMan test was ≥99.6% with all sample types. Reactivity with all HIV genotypes was 100%. LOD in plasma samples was 14.8, 12.6, and 27.9 copies/mL for HIV-1 group M, HIV-1 group O, and HIV-2, respectively, with similar results for serum samples. LOD in dried blood spots was 255 copies/mL for HIV-1 and 984 copies/mL for HIV-2. HIV infection was detected 18.9 days and 8.5 days earlier than the confirmatory and serological assays, respectively, and at a similar time to the NAT.
Conclusions: The cobas HIV-1/2 Qual test enables early and accurate diagnoses of HIV-1 and HIV-2 in adults and children across sample types. The assay could help avert transmission during acute HIV, simplify HIV diagnostic algorithms, and promote the survival of HIV-infected children.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- UNAIDS. Ending AIDS. Progress towards the 90-90-90 Targets. Global AIDS Update 2017. UNAIDS/JC2900E. 2017. Available at: http://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/Global_AIDS_update.... Accessed June 2019.
-
- UNAIDS. 90-90-90. An Ambitious Treatment Targetto Help End the AIDS Epidemic. UNAIDS/JC2684. 2014. Available at: http://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/90-90-90_en.pdf. Accessed June 2019.
-
- Cohen MS, Gay CL, Busch MP, et al. . The detection of acute HIV infection. J Infect Dis. 2010;202suppl 2:S270–S277. - PubMed
-
- Delaney KP, Hanson DL, Masciotra S, et al. . Time until emergence of HIV test reactivity following infection with HIV-1: implications for interpreting test results and retesting after exposure. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;64:53–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

