A Combination of RNA-Seq Analysis and Use of TCGA Database for Determining the Molecular Mechanism and Identifying Potential Drugs for GJB1 in Ovarian Cancer
- PMID: 33883906
- PMCID: PMC8055374
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S303589
A Combination of RNA-Seq Analysis and Use of TCGA Database for Determining the Molecular Mechanism and Identifying Potential Drugs for GJB1 in Ovarian Cancer
Abstract
Background: There has been increasing evidence for the vital role played by gap junction protein beta-1 (GJB1) in ovarian cancer (OC) and for the possibility of this protein serving as a therapeutic target. However, the detailed mechanism of GJB1 in OC has not yet been clearly determined. The current study aimed to establish the molecular mechanisms of the involvement of GJB1 in OC and to further predict potential drugs targeting this protein.
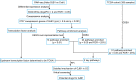
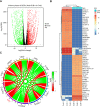
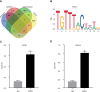
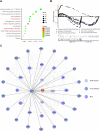
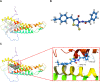
Methods: To better understand the molecular mechanisms of the involvement of GJB1 in OC, RNA-Seq transcriptome sequencing was performed. Then, we carried out an RNA-Seq analysis to determine the genes differentially co-expressed with GJB1. Subsequently, we carried out bioinformation methods to study the upstream regulatory transcriptional factor (TF) of GJB1. Further, the binding of FOXA1 and GJB1 promoter was tested using ChIP-qPCR. Moreover, we performed pathway enrichment to identify the downstream regulatory mechanisms of GJB1. Furthermore, potential drugs targeting GJB1 were screened using AutoDock 4.2.
Results: We constructed the transcriptional factor FOXA1 regulatory network based on the AnimalTFDB, JASPAR, RNA-Seq, TCGA cohort and ChIP-qPCR to study the upstream regulation of GJB1. In addition, two key pathways for the involvement of GJB1 in OC-namely the "ECM-receptor interaction" and "focal adhesion" KEGG pathways-were identified. Furthermore, ZINC000005552022 was found in a screening to be a potentially promising drug targeting GJB1.
Conclusion: Our study results suggested that the transcriptional factor FOXA1 regulates the involvement of GJB1 in OC through ECM-receptor interaction and focal adhesion KEGG pathways, and that ZINC000005552022 may have promising potential as a drug targeting GJB1; this finding might be used to help accelerate drug development and improve the outcomes for patients with OC.
Keywords: ChIP-qPCR; KEGG; omics; transcriptional factor; virtual screening.
© 2021 Yang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Yue H, Wang J, Chen R, Hou X, Li J, Lu X. Gene signature characteristic of elevated stromal infiltration and activation is associated with increased risk of hematogenous and lymphatic metastasis in serous ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer. 2019;19(1):1266. doi:10.1186/s12885-019-6470-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

