Solid-Pseudopapillary Neoplasm of the Pancreas: A 63-Case Analysis of Clinicopathologic and Immunohistochemical Features and Risk Factors of Malignancy
- PMID: 33883945
- PMCID: PMC8055352
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S304981
Solid-Pseudopapillary Neoplasm of the Pancreas: A 63-Case Analysis of Clinicopathologic and Immunohistochemical Features and Risk Factors of Malignancy
Abstract
Purpose: Solid-pseudopapillary neoplasm (SPN) of the pancreas, a rare tumor, has low malignant potential. However, some patients develop metastasis and recurrence after resection, with aggressive biological behaviors. This study aimed to explore the features and risk factors associated with the aggressive biological behaviors of SPNs.
Patients and methods: We retrospectively analyzed the clinicopathological and long-term follow-up data of 63 patients diagnosed with SPN at the First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College between January 2007 and February 2019.
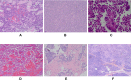
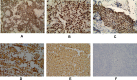
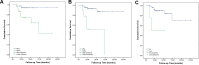
Results: Sixty-three patients presented atypical clinical symptoms. The median tumor size was 7.0 cm (range, 2.4-17 cm), and imaging features were solid and cystic or solid tumors with uneven density. Frequent and diffuse nuclear LEF1 protein expression (94.2%) was observed with LEF1 having a higher sensitivity and specificity. Overall survival significantly correlated with tumor size, Ki-67 index, and lymph node metastasis (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: SPN is a rare low-grade malignancy with a specific pseudopapillary structure. LEF1 is an effective biomarker of SPNs. Although SPNs generally display indolent biological behavior, a large tumor size, high proliferation index, and lymph node metastasis may be risk factors for the aggressive behavior and poor prognosis of SPN.
Keywords: LEF1; metastasis; overall survival; pancreatic tumor; retrospective study.
© 2021 Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic insights into solid pseudopapillary neoplasms of the pancreas: a decade of experience with pediatric representation.Diagn Pathol. 2025 Apr 30;20(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s13000-025-01648-9. Diagn Pathol. 2025. PMID: 40307756 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of solid pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas: comparison between tumors ≤5 cm and larger tumors].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2016 Jun;36(6):780-4. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2016. PMID: 27320878 Chinese.
-
Long-term Survival, Quality of Life, and Molecular Features of the Patients With Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm of the Pancreas: A Retrospective Study of 454 Cases.Ann Surg. 2023 Dec 1;278(6):1009-1017. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000005842. Epub 2023 Apr 10. Ann Surg. 2023. PMID: 37036095
-
Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm (SPN) of the pancreas: current understanding on its malignant potential and management.Discov Oncol. 2024 Mar 18;15(1):77. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-00905-5. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38498246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study of 29 cases of solid-pseudopapillary neoplasms of the pancreas in patients under 20 years of age along with detailed review of literature.Diagn Pathol. 2020 Dec 9;15(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s13000-020-01058-z. Diagn Pathol. 2020. PMID: 33298094 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Current highlights on solid pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas.World J Hepatol. 2022 Jan 27;14(1):300-303. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i1.300. World J Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35126857 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the enigma: A comprehensive review of solid pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Mar 15;16(3):614-629. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i3.614. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38577449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas with hepatic metastases: problems and strategies.Front Oncol. 2024 Jul 19;14:1410888. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1410888. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39099687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Sex Features of Patients With Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasms of the Pancreas: A Retrospective Study.Front Oncol. 2022 Feb 18;12:844182. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.844182. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35252013 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic utility of LEF1 and β-catenin in WNT pathway tumors with CTNNB1 mutation.World J Surg Oncol. 2025 Jan 29;23(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s12957-025-03675-8. World J Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39881334 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

