Serum Tyrosine Level in Acute Murine Toxoplasmosis
- PMID: 33884014
- PMCID: PMC8039484
- DOI: 10.18502/ijpa.v15i4.4866
Serum Tyrosine Level in Acute Murine Toxoplasmosis
Abstract
Background: Toxoplasmosis is a zoonotic disease caused by the obligate intracellular parasite, Toxoplasma gondii. This global infectious disease has been associated with behavioral changes in rodents and can result in humans' neuropsychiatric symptoms. Since the neurotransmitters alteration can cause a behavioral change, in this study, tyrosine level, as a precursor of dopamine, was evaluated in acute murine toxoplasmosis during 2015 and 2016 in Shiraz, Iran.
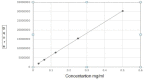
Methods: At the first, 105 tachyzoites of T. gondii were subcutaneously inoculated to 50 BALB/c mice as experimental groups and 10 mice inoculated by PBS considered as the control group. After that, daily, one group of mice was bled, and sera were collected. Then, their serum tyrosine level was evaluated by HPLC method.
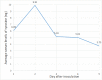
Results: After data analysis, the maximum mean serum tyrosine level was seen at 2th day of post parasite inoculation (0.0194 mg/ ml), with a significant difference compared to the control group (0.0117 mg/ ml, P=0.025). Moreover, the least quantity of serum tyrosine (0.076 mg/ml) was seen on the 5th day, after parasite inoculation, however, no significant difference was seen.
Conclusion: Serum tyrosine level increased in 2 d after inoculation of Toxoplasma, but the level regularly decreased in successive days. Tyrosine level increased by phenylalanine hydroxylase 2 days after inoculation, then tyrosine decreased by tyrosine hydroxylase in the next days. Toxoplasma tyrosine hydroxylase enzymes, at primary days of toxoplasmosis, effect on tyrosine production, and after that, the most effect on tyrosine consumption.
Keywords: High-performance liquid chromatography; Mice; Toxoplasma gondii; Tyrosine.
Copyright © 2020 Asgari et al. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dubey J, Jones J. Toxoplasma gondii infection in humans and animals in the United States. Int J Parasitol. 2008;38(11):1257–78. - PubMed
-
- Dunn D, Wallon M, Peyron F, et al. Mother-to-child transmission of toxoplasmosis: risk estimates for clinical counselling. Lancet. 1999;353(9167):1829–33. - PubMed
-
- Flegr J. How and why Toxoplasma makes us crazy. Trends Parasitol. 2013;29(4):156–63. - PubMed
-
- Fekadu A, Shibre T, Cleare AJ. Toxoplasmosis as a cause for behavior disorders-overview of evidence and mechanisms. Folia Parasitol (Praha). 2010;57(2):105–13. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources