Effect of Moxibustion on β-EP and Dyn Levels of Pain-Related Indicators in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 33884025
- PMCID: PMC8041546
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6637554
Effect of Moxibustion on β-EP and Dyn Levels of Pain-Related Indicators in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic immunodeficiency disease characterized by persistent synovial inflammation, pannus formation, and bone and cartilage destruction, resulting in joint malformations and function decline.
Objective: The purpose of this study is to evaluate the effect of moxibustion on clinical symptoms and levels of pain-related indicators beta-endorphin (β-EP) and dynorphin (Dyn) in patients with RA and to explore the potential anti-inflammatory and analgesic mechanisms of moxibustion in RA treatment.
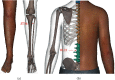
Methods: A total of 64 patients with RA who met the inclusion criteria were randomly and equally classified into the control and treatment groups. The control group received conventional treatment (oral methotrexate, folate, or leflunomide prescribed for a long time). The treatment group was treated with moxibustion at ST36 (Zusanli), BL23 (Shenshu), and Ashi points with respect to the control group. Patients' clinical symptoms and routine inspection indexes (rheumatoid factor [RF], erythrocyte sedimentation rate [ESR], and C-reactive protein [CRP]) were recorded before and after treatment. Serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), β-EP, and Dyn were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The software SPSS24.0 was used for statistical analysis.
Results: (1) Compared with the pretreatment result, both of the two groups' clinical symptoms and routine inspection indexes (RF, ESR, and CRP) improved (P < 0.05), and the improvement of clinical symptoms in the treatment group outperformed that in the control group (P < 0.05). (2) TNF-α and IL-1β levels decreased significantly in the treatment group after treatment (P < 0.01), while no significant difference was observed in the control group (P > 0.05). (3) β-EP and Dyn levels in the treatment group were significantly increased after treatment (P < 0.01, P < 0.01), but the control group showed no significant difference (P > 0.05, P > 0.05). It is worth mentioning that the serum TNF-α, IL-1β, β-EP, and Dyn levels between the two groups were significantly different after 8 weeks of treatment (P < 0.05). (4) Differences in the serum β-EP and Dyn levels in the patients of the treatment group were correlated with TNF-α and IL-1β levels after treatment, and the correlation was mainly negative (r < 0).
Conclusion: Moxibustion can improve joint pain in patients with RA using conventional western medicine. One of the mechanisms may affect the serum β-EP and Dyn levels by downregulating the inflammatory factors to play an anti-inflammatory and analgesic role.
Copyright © 2021 Yingni Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Regulatory effect of moxibustion on LTB4/MMP-9 in serum of patients with rheumatoid arthritis].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2023 May 25;48(5):488-93. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20220088. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2023. PMID: 37247863 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
The Efficacy of Moxibustion on the Serum Levels of CXCL1 and β-EP in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.Pain Res Manag. 2021 Oct 13;2021:7466313. doi: 10.1155/2021/7466313. eCollection 2021. Pain Res Manag. 2021. PMID: 34691317 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Moxibustion on the Serum Levels of MMP-1, MMP-3, and VEGF in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Sep 16;2020:7150605. doi: 10.1155/2020/7150605. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 33014110 Free PMC article.
-
Moxibustion regulates the polarization of macrophages through the IL-4/STAT6 pathway in rheumatoid arthritis.Cytokine. 2022 Apr;152:155835. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2022.155835. Epub 2022 Feb 28. Cytokine. 2022. PMID: 35240467 Review.
-
[Effects of moxibustion on serum cytokines in experimental animals with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2020 Sep 25;45(9):751-61. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.190780. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2020. PMID: 32959560 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Effect of chrono-moxibustion and its influence on circadian rhythm for rheumatoid arthritis: A study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Sep 23;101(38):e30701. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000030701. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36197183 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of efficacy of different combination therapies of α-receptor blockers and traditional Chinese medicine external therapy in the treatment of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: Bayesian network meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Apr 20;18(4):e0280821. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280821. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37079509 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Efficacy of Acupuncture-Related Therapy in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 7;13:829409. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.829409. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35320944 Free PMC article.
-
Moxibustion as an Adjuvant Therapy for Cancer Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Pain Res. 2023 Feb 17;16:515-525. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S396696. eCollection 2023. J Pain Res. 2023. PMID: 36824500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Formation of a β-Endorphin Corona Mitigates Alzheimer's Amyloidogenesis.Small. 2025 Jul;21(26):e2409392. doi: 10.1002/smll.202409392. Epub 2025 May 19. Small. 2025. PMID: 40384186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Naqvi A. A., Hassali M. A., Aftab M. T. Epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis, clinical aspects and socio-economic determinants in Pakistani patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Pakistan Medical Association. 2019;69(3):389–398. - PubMed
-
- Wasserman A. M. Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis. American Family Physician. 2011;84(11):1245–1252. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

