Introducing CASCADEPOP: an open-source sociodemographic simulation platform for us health policy appraisal
- PMID: 33884027
- PMCID: PMC8057701
- DOI: 10.34196/ijm.00217
Introducing CASCADEPOP: an open-source sociodemographic simulation platform for us health policy appraisal
Abstract
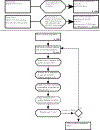
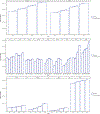
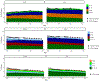
Largescale individual-level and agent-based models are gaining importance in health policy appraisal and evaluation. Such models require the accurate depiction of the jurisdiction's population over extended time periods to enable modeling of the development of non-communicable diseases under consideration of historical, sociodemographic developments. We developed CASCADEPOP to provide a readily available sociodemographic micro-synthesis and microsimulation platform for US populations. The micro-synthesis method used iterative proportional fitting to integrate data from the US Census, the American Community Survey, the Panel Study of Income Dynamics, Multiple Cause of Death Files, and several national surveys to produce a synthetic population aged 12 to 80 years on 01/01/1980 for five states (California, Minnesota, New York, Tennessee, and Texas) and the US. Characteristics include individuals' age, sex, race/ethnicity, marital/employment/parental status, education, income and patterns of alcohol use as an exemplar health behavior. The microsimulation simulates individuals' sociodemographic life trajectories over 35 years to 31/12/2015 accounting for population developments including births, deaths, and migration. Results comparing the 1980 micro-synthesis against observed data shows a successful depiction of state and US population characteristics and of drinking. Comparing the microsimulation over 30 years with Census data also showed the successful simulation of sociodemographic developments. The CASCADEPOP platform enables modelling of health behaviors across individuals' life courses and at a population level. As it contains a large number of relevant sociodemographic characteristics it can be further developed by researchers to build US agent-based models and microsimulations to examine health behaviors, interventions, and policies.
Keywords: AGENT-BASED MODELING; ALCOHOL USE; DEMOGRAPHY; MICROSIMULATION MODELS; PUBLIC HEALTH; SOCIAL SIMULATION; UNITED STATES.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Simulation of Alcohol Control Policies for Health Equity (SIMAH) Project: Study Design and First Results.Am J Epidemiol. 2023 May 5;192(5):690-702. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwad018. Am J Epidemiol. 2023. PMID: 36702471 Free PMC article.
-
An open-source and spatially diverse synthetic population dataset for agent-based modelling and microsimulation in Ireland.Data Brief. 2025 May 1;60:111611. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2025.111611. eCollection 2025 Jun. Data Brief. 2025. PMID: 40486220 Free PMC article.
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
Comparison of US County-Level Public Health Performance Rankings With County Cluster and National Rankings: Assessment Based on Prevalence Rates of Smoking and Obesity and Motor Vehicle Crash Death Rates.JAMA Netw Open. 2019 Jan 4;2(1):e186816. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2018.6816. JAMA Netw Open. 2019. PMID: 30646196 Free PMC article.
-
Projecting the effects of tobacco control policies in the USA through microsimulation: a study protocol.BMJ Open. 2018 Mar 23;8(3):e019169. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-019169. BMJ Open. 2018. PMID: 29574440 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Simulation of Alcohol Control Policies for Health Equity (SIMAH) Project: Study Design and First Results.Am J Epidemiol. 2023 May 5;192(5):690-702. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwad018. Am J Epidemiol. 2023. PMID: 36702471 Free PMC article.
-
Commentary on Robinson et al. (2021): Evaluating theories of change for public health policies using computer model discovery methods.Addiction. 2021 Oct;116(10):2709-2711. doi: 10.1111/add.15595. Epub 2021 Jun 28. Addiction. 2021. PMID: 34184346 Free PMC article.
-
Can Social Norms Explain Long-Term Trends in Alcohol Use? Insights from Inverse Generative Social Science.J Artif Soc Soc Simul. 2023;26(2):4. doi: 10.18564/jasss.5077. Epub 2023 Mar 31. J Artif Soc Soc Simul. 2023. PMID: 37235176 Free PMC article.
-
Causality and initiation of alcohol control policy. A response to Allamani.Drug Alcohol Rev. 2021 Nov;40(7):1389-1391. doi: 10.1111/dar.13371. Epub 2021 Aug 4. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2021. PMID: 34347331 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of agent-based modeling in trauma research.Psychol Trauma. 2023 Sep;15(6):939-950. doi: 10.1037/tra0001375. Epub 2022 Sep 22. Psychol Trauma. 2023. PMID: 36136775 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bai H, Brennan A, Broomhead T, Meier PS, Nielsen A, Probst C, Vu TM, & Purshouse RC (2019). Modeling alcohol use behavior at population scale based on social role theory: An exploratory agent-based model. HEDS Discussion Paper 17/04.
-
- Ballas D, Clarke G, Dorling D, & Rossiter D (2007). Using SimBritain to model the geographical impact of national government policies. Geographical Analysis, 39(1), 44–77.
-
- Blocker AW (2016). Package ‘ipfp’.
-
- Brennan A, Meier P, Purshouse R, Rafia R, Meng Y, Hill-Macmanus D, Angus C, & Holmes J (2015). The Sheffield alcohol policy model–a mathematical description. Health Economics, 24(10), 1368–1388. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics. Compressed Mortality File. (1979). 1979–1998. CDC WONDER On-line Database, compiled from Compressed Mortality File CMF 1968–1988, Series 20, No. 2A, 2000 and CMF 1989–1998, Series 20, No. 2E, 2003. Accessed at http://wonder.cdc.gov/cmf-icd9.html on Jun 20, 2019 6:04:42 AM.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
