Integrating Metacognitive Regulation into the Online Classroom Using Student-Developed Learning Plans
- PMID: 33884055
- PMCID: PMC8011874
- DOI: 10.1128/jmbe.v22i1.2409
Integrating Metacognitive Regulation into the Online Classroom Using Student-Developed Learning Plans
Abstract
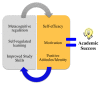
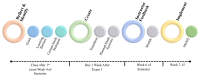
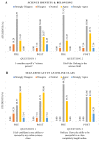
Students and instructors have been faced with unexpected challenges that presented rapidly due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The pandemic forced students into an unfamiliar learning ecosystem to which they had to quickly adapt in order to continue to be successful in their courses. Literature supports the importance of metacognition and self-regulated learning in the success of students in an online environment. More importantly, the concept of metacognitive regulation, which includes monitoring, planning, executing, and adapting learning strategies, is vital to student academic success. These strategies have been shown to close the opportunity gap observed specifically in persons excluded because of their ethnicity or race (PEERs) in STEM. Outlined here is the use of student-developed learning plans as a guided process to enhance students' metacognitive regulation of their learning. These learning plans provide students a template to assist them in time management, practical study skills and planned study sessions, that are designed to increase their self-efficacy, motivation, and performance in online classes. Moreover, the iterative nature of the learning plan encourages students to continue to use and expand this plan in other academic courses.
©2021 Author(s). Published by the American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
References
-
- Adedoyin OB, Soykan E. COVID-19 pandemic and online learning: the challenges and opportunities. Interact Learn Environ. 2020 doi: 10.1080/10494820.2020.1813180. - DOI
-
- Cho MH, Shen D. Self-regulation in online learning. Dist Educ. 2013;34(3)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
