Performance of GeneXpert MTB/RIF for Diagnosing Tuberculosis Among Symptomatic Household Contacts of Index Patients in South Africa
- PMID: 33884274
- PMCID: PMC8047860
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofab025
Performance of GeneXpert MTB/RIF for Diagnosing Tuberculosis Among Symptomatic Household Contacts of Index Patients in South Africa
Abstract
Background: We describe the performance of GeneXpert MTB/RIF (Xpert) for diagnosing tuberculosis (TB) among symptomatic household contacts (HHCs) of rifampicin-resistant and drug-sensitive index cases.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study among HHCs of recently diagnosed (<2 weeks) smear-positive and Xpert-positive index cases in the Bojanala District, South Africa. The HHCs were screened for TB symptoms; persons with ≥1 TB symptom provided 1 sputum for smear microscopy, Xpert, and mycobacterial growth indicator tube (MGIT) culture. Diagnostic test performance of Xpert was determined using MGIT as the reference standard.
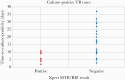
Results: From August 2013 to July 2015, 619 HHCs from 216 index cases were enrolled: 60.6% were female, median age was 22 years (interquartile range, 9-40), and 126 (20.4%) self-reported/tested human immunodeficiency virus positive. A total of 54.3% (336 of 619) of contacts had ≥1 TB symptom (cough, fever, night sweats, weight loss), 297 of 336 (88.4%) of which provided a sputum; 289 (97.3%) had complete testing and 271 were included in the analysis. In total, 42 (6.8%) of 619 HHCs had microbiologically confirmed TB. The MGIT identified 33 HHCs as positive for Mycobacterium tuberculosis; of these, 7 were positive on Xpert resulting in a sensitivity of 21.2% (95% confidence interval [CI], 9.0-38.9), specificity of 98.3% (95% CI, 95.6-99.5), positive predictive value of 63.6% (95% CI, 30.8-89.1), and negative predictive value of 90.0 (95% CI, 85.7-93.4).
Conclusions: Among symptomatic HHCs investigated for TB, Xpert performed suboptimally compared with MGIT culture. The poor performance of Xpert for diagnosing TB suggests that a more sensitive test, such a Xpert Ultra or culture, may be needed to improve yield of contact investigation, where feasible.
Keywords: GeneXpert MTB/RIF; TB disease; household contacts; mycobacterial culture.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2019.
-
- Ayles H, Muyoyeta M, Du Toit E, et al. ; ZAMSTAR team. Effect of household and community interventions on the burden of tuberculosis in southern Africa: the ZAMSTAR community-randomised trial. Lancet 2013; 382:1183–94. - PubMed
-
- Fox GJ, Nhung NV, Sy DN, et al. . Household-contact investigation for detection of tuberculosis in Vietnam. N Engl J Med 2018; 378:221–9. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Systematic Screening for Active Tuberculosis: Principles and Recommendations. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources