Effects of Behavioral Weight Loss and Metformin on IGFs in Cancer Survivors: A Randomized Trial
- PMID: 33884414
- PMCID: PMC8475239
- DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgab266
Effects of Behavioral Weight Loss and Metformin on IGFs in Cancer Survivors: A Randomized Trial
Abstract
Context: Higher levels of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) are associated with increased risk of cancers and higher mortality. Therapies that reduce IGF-1 have considerable appeal as means to prevent recurrence.
Design: Randomized, 3-parallel-arm controlled clinical trial.
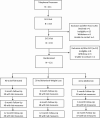
Interventions and outcomes: Cancer survivors with overweight or obesity were randomized to (1) self-directed weight loss (comparison), (2) coach-directed weight loss, or (3) metformin treatment. Main outcomes were changes in IGF-1 and IGF-1:IGFBP3 molar ratio at 6 months. The trial duration was 12 months.
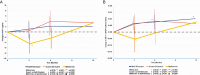
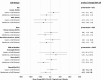
Results: Of the 121 randomized participants, 79% were women, 46% were African Americans, and the mean age was 60 years. At baseline, the average body mass index was 35 kg/m2; mean IGF-1 was 72.9 (SD, 21.7) ng/mL; and mean IGF1:IGFBP3 molar ratio was 0.17 (SD, 0.05). At 6 months, weight changes were -1.0% (P = 0.07), -4.2% (P < 0.0001), and -2.8% (P < 0.0001) in self-directed, coach-directed, and metformin groups, respectively. Compared with the self-directed group, participants in metformin had significant decreases on IGF-1 (mean difference in change: -5.50 ng/mL, P = 0.02) and IGF1:IGFBP3 molar ratio (mean difference in change: -0.0119, P = 0.011) at 3 months. The significant decrease of IGF-1 remained in participants with obesity at 6 months (mean difference in change: -7.2 ng/mL; 95% CI: -13.3 to -1.1), but not in participants with overweight (P for interaction = 0.045). There were no significant differences in changes between the coach-directed and self-directed groups. There were no differences in outcomes at 12 months.
Conclusions: In cancer survivors with obesity, metformin may have a short-term effect on IGF-1 reduction that wanes over time.
Keywords: IGF-1; IGFBP3; behavioral weight loss; insulin-like growth factors; metformin; weight.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of a Behavioral Weight Loss Intervention and Metformin Treatment on Serum Urate: Results from a Randomized Clinical Trial.Nutrients. 2021 Jul 31;13(8):2673. doi: 10.3390/nu13082673. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34444833 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phase II study of metformin for reduction of obesity-associated breast cancer risk: a randomized controlled trial protocol.BMC Cancer. 2016 Jul 19;16:500. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2551-3. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27430256 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of dietary weight loss and exercise on insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 in postmenopausal women: a randomized controlled trial.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2013 Aug;22(8):1457-63. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-13-0337. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2013. PMID: 23756654 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Obesity Management in Women.Nurs Clin North Am. 2024 Dec;59(4):593-609. doi: 10.1016/j.cnur.2024.08.005. Epub 2024 Sep 23. Nurs Clin North Am. 2024. PMID: 39477566 Review.
-
Mechanisms of ageing: growth hormone, dietary restriction, and metformin.Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023 Apr;11(4):261-281. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(23)00001-3. Epub 2023 Feb 24. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023. PMID: 36848915 Review.
Cited by
-
Interventions for weight reduction in obesity to improve survival in women with endometrial cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Mar 27;3(3):CD012513. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012513.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36971688 Free PMC article.
-
Current status and frontier tracking of clinical trials on Metformin for cancer treatment.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Dec;149(18):16931-16946. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05391-w. Epub 2023 Sep 12. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37698682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of a Behavioral Weight Loss Intervention and Metformin Treatment on Serum Urate: Results from a Randomized Clinical Trial.Nutrients. 2021 Jul 31;13(8):2673. doi: 10.3390/nu13082673. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34444833 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Metformin and the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway: implications for cancer, cardiovascular, and central nervous system diseases.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Feb;398(2):1035-1055. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03358-3. Epub 2024 Sep 3. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39225830 Review.
-
Metformin Affects Gut Microbiome Composition and Function and Circulating Short-Chain Fatty Acids: A Randomized Trial.Diabetes Care. 2021 Jul;44(7):1462-1471. doi: 10.2337/dc20-2257. Epub 2021 May 18. Diabetes Care. 2021. PMID: 34006565 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Renehan AG, Zwahlen M, Egger M. Adiposity and cancer risk: new mechanistic insights from epidemiology. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015;15(8):484-498. - PubMed
-
- Renehan AG, Zwahlen M, Minder C, O’Dwyer ST, Shalet SM, Egger M. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF binding protein-3, and cancer risk: systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Lancet. 2004;363(9418):1346-1353. - PubMed
-
- Decensi A, Puntoni M, Goodwin P, et al. . Metformin and cancer risk in diabetic patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2010;3(11):1451-1461. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

