Maternal and Neonatal Morbidity and Mortality Among Pregnant Women With and Without COVID-19 Infection: The INTERCOVID Multinational Cohort Study
- PMID: 33885740
- PMCID: PMC8063132
- DOI: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2021.1050
Maternal and Neonatal Morbidity and Mortality Among Pregnant Women With and Without COVID-19 Infection: The INTERCOVID Multinational Cohort Study
Erratum in
-
Misspelled Author Name in the Byline.JAMA Pediatr. 2022 Jan 1;176(1):104. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2021.4953. JAMA Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 34779828 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Importance: Detailed information about the association of COVID-19 with outcomes in pregnant individuals compared with not-infected pregnant individuals is much needed.
Objective: To evaluate the risks associated with COVID-19 in pregnancy on maternal and neonatal outcomes compared with not-infected, concomitant pregnant individuals.
Design, setting, and participants: In this cohort study that took place from March to October 2020, involving 43 institutions in 18 countries, 2 unmatched, consecutive, not-infected women were concomitantly enrolled immediately after each infected woman was identified, at any stage of pregnancy or delivery, and at the same level of care to minimize bias. Women and neonates were followed up until hospital discharge.
Exposures: COVID-19 in pregnancy determined by laboratory confirmation of COVID-19 and/or radiological pulmonary findings or 2 or more predefined COVID-19 symptoms.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary outcome measures were indices of (maternal and severe neonatal/perinatal) morbidity and mortality; the individual components of these indices were secondary outcomes. Models for these outcomes were adjusted for country, month entering study, maternal age, and history of morbidity.
Results: A total of 706 pregnant women with COVID-19 diagnosis and 1424 pregnant women without COVID-19 diagnosis were enrolled, all with broadly similar demographic characteristics (mean [SD] age, 30.2 [6.1] years). Overweight early in pregnancy occurred in 323 women (48.6%) with COVID-19 diagnosis and 554 women (40.2%) without. Women with COVID-19 diagnosis were at higher risk for preeclampsia/eclampsia (relative risk [RR], 1.76; 95% CI, 1.27-2.43), severe infections (RR, 3.38; 95% CI, 1.63-7.01), intensive care unit admission (RR, 5.04; 95% CI, 3.13-8.10), maternal mortality (RR, 22.3; 95% CI, 2.88-172), preterm birth (RR, 1.59; 95% CI, 1.30-1.94), medically indicated preterm birth (RR, 1.97; 95% CI, 1.56-2.51), severe neonatal morbidity index (RR, 2.66; 95% CI, 1.69-4.18), and severe perinatal morbidity and mortality index (RR, 2.14; 95% CI, 1.66-2.75). Fever and shortness of breath for any duration was associated with increased risk of severe maternal complications (RR, 2.56; 95% CI, 1.92-3.40) and neonatal complications (RR, 4.97; 95% CI, 2.11-11.69). Asymptomatic women with COVID-19 diagnosis remained at higher risk only for maternal morbidity (RR, 1.24; 95% CI, 1.00-1.54) and preeclampsia (RR, 1.63; 95% CI, 1.01-2.63). Among women who tested positive (98.1% by real-time polymerase chain reaction), 54 (13%) of their neonates tested positive. Cesarean delivery (RR, 2.15; 95% CI, 1.18-3.91) but not breastfeeding (RR, 1.10; 95% CI, 0.66-1.85) was associated with increased risk for neonatal test positivity.
Conclusions and relevance: In this multinational cohort study, COVID-19 in pregnancy was associated with consistent and substantial increases in severe maternal morbidity and mortality and neonatal complications when pregnant women with and without COVID-19 diagnosis were compared. The findings should alert pregnant individuals and clinicians to implement strictly all the recommended COVID-19 preventive measures.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
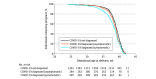
Comment in
-
COVID-19 in Pregnant Women and Their Newborn Infants.JAMA Pediatr. 2021 Aug 1;175(8):781-783. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2021.1046. JAMA Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 33885744 No abstract available.
-
Further Observations on Pregnancy Complications and COVID-19 Infection.JAMA Pediatr. 2021 Nov 1;175(11):1185. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2021.2613. JAMA Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34398214 No abstract available.
-
Further Observations on Pregnancy Complications and COVID-19 Infection.JAMA Pediatr. 2021 Nov 1;175(11):1184-1185. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2021.2609. JAMA Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34398227 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Yap M, Debenham L, Kew T, et al. ; PregCOV-19 Consortium . Clinical manifestations, prevalence, risk factors, outcomes, transmission, diagnosis and treatment of COVID-19 in pregnancy and postpartum: a living systematic review protocol. BMJ Open. 2020;10(12):e041868. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-041868 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Knight M, Bunch K, Vousden N, et al. ; UK Obstetric Surveillance System SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Pregnancy Collaborative Group . Characteristics and outcomes of pregnant women admitted to hospital with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection in UK: national population based cohort study. BMJ. 2020;369:m2107. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m2107 - DOI - PMC - PubMed

