Histone sumoylation and chromatin dynamics
- PMID: 33885816
- PMCID: PMC8216275
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkab280
Histone sumoylation and chromatin dynamics
Abstract
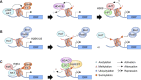
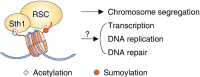
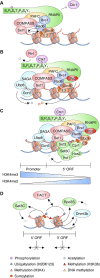
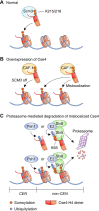
Chromatin structure and gene expression are dynamically controlled by post-translational modifications (PTMs) on histone proteins, including ubiquitylation, methylation, acetylation and small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) conjugation. It was initially thought that histone sumoylation exclusively suppressed gene transcription, but recent advances in proteomics and genomics have uncovered its diverse functions in cotranscriptional processes, including chromatin remodeling, transcript elongation, and blocking cryptic initiation. Histone sumoylation is integral to complex signaling codes that prime additional histone PTMs as well as modifications of the RNA polymerase II carboxy-terminal domain (RNAPII-CTD) during transcription. In addition, sumoylation of histone variants is critical for the DNA double-strand break (DSB) response and for chromosome segregation during mitosis. This review describes recent findings on histone sumoylation and its coordination with other histone and RNAPII-CTD modifications in the regulation of chromatin dynamics.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Trans-tail regulation-mediated suppression of cryptic transcription.Exp Mol Med. 2021 Nov;53(11):1683-1688. doi: 10.1038/s12276-021-00711-x. Epub 2021 Nov 29. Exp Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34845331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Priming chromatin for segregation: functional roles of mitotic histone modifications.Cell Cycle. 2020 Mar;19(6):625-641. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1719585. Epub 2020 Jan 28. Cell Cycle. 2020. PMID: 31992120 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Ulp2 SUMO protease promotes transcription elongation through regulation of histone sumoylation.EMBO J. 2019 Aug 15;38(16):e102003. doi: 10.15252/embj.2019102003. Epub 2019 Jul 17. EMBO J. 2019. PMID: 31313851 Free PMC article.
-
Sumoylation of the human histone H4 tail inhibits p300-mediated transcription by RNA polymerase II in cellular extracts.Elife. 2021 Nov 8;10:e67952. doi: 10.7554/eLife.67952. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34747692 Free PMC article.
-
Modifications of RNA polymerase II CTD: Connections to the histone code and cellular function.Biotechnol Adv. 2015 Nov 1;33(6 Pt 1):856-72. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.07.008. Epub 2015 Aug 1. Biotechnol Adv. 2015. PMID: 26241863 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of SUMOylation on RNA metabolism in cancers.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Feb 24;10:1137215. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1137215. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36911524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Total chemical synthesis of sumoylated histone H4 reveals negative biochemical crosstalk with histone ubiquitylation.Chem Commun (Camb). 2023 Mar 30;59(27):4063-4066. doi: 10.1039/d2cc06683a. Chem Commun (Camb). 2023. PMID: 36938583 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer-Associated Dysregulation of Sumo Regulators: Proteases and Ligases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 20;23(14):8012. doi: 10.3390/ijms23148012. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic modifications involving ncRNAs in digestive system cancers: focus on histone modification.Clin Epigenetics. 2024 Nov 19;16(1):162. doi: 10.1186/s13148-024-01773-0. Clin Epigenetics. 2024. PMID: 39563475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRIM28-dependent SUMOylation protects the adult ovary from activation of the testicular pathway.Nat Commun. 2022 Jul 29;13(1):4412. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32061-1. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35906245 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johnson E.S. Protein modification by SUMO. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2004; 73:355–382. - PubMed
-
- Huang W.C., Ko T.P., Li S.S., Wang A.H.. Crystal structures of the human SUMO-2 protein at 1.6 A and 1.2 A resolution: implication on the functional differences of SUMO proteins. Eur. J. Biochem. 2004; 271:4114–4122. - PubMed
-
- Johnson P.R., Hochstrasser M.. SUMO-1: ubiquitin gains weight. Trends Cell Biol. 1997; 7:408–413. - PubMed
-
- Owerbach D., McKay E.M., Yeh E.T.H., Gabbay K.H., Bohren K.M.. A proline-90 residue unique to SUMO-4 prevents maturation and sumoylation. Biochem Bioph Res Co. 2005; 337:517–520. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

