Growth differentiation factor 11: a "rejuvenation factor" involved in regulation of age-related diseases?
- PMID: 33886503
- PMCID: PMC8109099
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.202881
Growth differentiation factor 11: a "rejuvenation factor" involved in regulation of age-related diseases?
Abstract
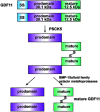
Growth differentiation factor 11 (GDF11), a member of the transforming growth factor β superfamily of cytokines, is a critical rejuvenation factor in aging cells. GDF11 improves neurodegenerative and neurovascular disease outcomes, increases skeletal muscle volume, and enhances muscle strength. Its wide-ranging biological effects may include the reversal of senescence in clinical applications, as well as the ability to reverse age-related pathological changes and regulate organ regeneration after injury. Nevertheless, recent data have led to controversy regarding the functional roles of GDF11, because the underlying mechanisms were not clearly established in previous studies. In this review, we examine the literature regarding GDF11 in age-related diseases and discuss potential mechanisms underlying the effects of GDF11 in regulation of age-related diseases.
Keywords: GDF11; age-related diseases; aging; growth differentiation factor 11; regeneration; transforming growth factor.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
GDF11 Increases with Age and Inhibits Skeletal Muscle Regeneration.Cell Metab. 2015 Jul 7;22(1):164-74. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.05.010. Epub 2015 May 19. Cell Metab. 2015. PMID: 26001423 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted myocardial delivery of GDF11 gene rejuvenates the aged mouse heart and enhances myocardial regeneration after ischemia-reperfusion injury.Basic Res Cardiol. 2017 Jan;112(1):7. doi: 10.1007/s00395-016-0593-y. Epub 2016 Dec 21. Basic Res Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28004242
-
A GDF11/myostatin inhibitor, GDF11 propeptide-Fc, increases skeletal muscle mass and improves muscle strength in dystrophic mdx mice.Skelet Muscle. 2019 May 27;9(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13395-019-0197-y. Skelet Muscle. 2019. PMID: 31133057 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Potential of GDF11: Myth or Reality?Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 21;20(14):3563. doi: 10.3390/ijms20143563. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31330871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Growth Differentiation Factor 11 (GDF11) and Myostatin (MSTN) in tissue specific aging.Mech Ageing Dev. 2017 Jun;164:108-112. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2017.04.009. Epub 2017 May 1. Mech Ageing Dev. 2017. PMID: 28472635 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential Satellite Cell-Linked Biomarkers in Aging Skeletal Muscle Tissue: Proteomics and Proteogenomics to Monitor Sarcopenia.Proteomes. 2022 Aug 19;10(3):29. doi: 10.3390/proteomes10030029. Proteomes. 2022. PMID: 35997441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loss of Growth Differentiation Factor 11 Shortens Telomere Length by Downregulating Telomerase Activity.Front Physiol. 2021 Sep 13;12:726345. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.726345. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34588995 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of the geroprotective cytokine on the transcriptome of young and senescent mesenchymal stem cells.BMC Res Notes. 2025 Apr 24;18(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s13104-025-07262-8. BMC Res Notes. 2025. PMID: 40275319 Free PMC article.
-
Natural saponins and macrophage polarization: Mechanistic insights and therapeutic perspectives in disease management.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 9;16:1584035. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1584035. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40417220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GDF11: An emerging therapeutic target for liver diseases and fibrosis.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Apr;28(7):e18140. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18140. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38494851 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sertedaki E, Veroutis D, Zagouri F, Galyfos G, Filis K, Papalambros A, Aggeli K, Tsioli P, Charalambous G, Zografos G, Sigala F. Carotid Disease and Ageing: A Literature Review on the Pathogenesis of Vascular Senescence in Older Subjects. Curr Gerontol Geriatr Res. 2020; 2020:8601762. 10.1155/2020/8601762 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

