Pyrenophora teres: Taxonomy, Morphology, Interaction With Barley, and Mode of Control
- PMID: 33889162
- PMCID: PMC8055952
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2021.614951
Pyrenophora teres: Taxonomy, Morphology, Interaction With Barley, and Mode of Control
Abstract
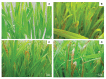
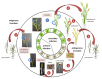
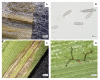
Net blotch, induced by the ascomycete Pyrenophora teres, has become among the most important disease of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Easily recognizable by brown reticulated stripes on the sensitive barley leaves, net blotch reduces the yield by up to 40% and decreases seed quality. The life cycle, the mode of dispersion and the development of the pathogen, allow a quick contamination of the host. Crop residues, seeds, and wild grass species are the inoculum sources to spread the disease. The interaction between the barley plant and the fungus is complex and involves physiological changes with the emergence of symptoms on barley and genetic changes including the modulation of different genes involved in the defense pathways. The genes of net blotch resistance have been identified and their localizations are distributed on seven barley chromosomes. Considering the importance of this disease, several management approaches have been performed to control net blotch. One of them is the use of beneficial bacteria colonizing the rhizosphere, collectively referred to as Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria. Several studies have reported the protective role of these bacteria and their metabolites against potential pathogens. Based on the available data, we expose a comprehensive review of Pyrenophora teres including its morphology, interaction with the host plant and means of control.
Keywords: Hordeum vulgare L.; Pyrenophora teres; barley; net blotch; plant growth promoting rhizobacteria.
Copyright © 2021 Backes, Guerriero, Ait Barka and Jacquard.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Adawy S. S., Diab A. A., Sayed A. H. I., Ibrahim S. D., El-Morsy S. I., Saker M. M. (2013). Construction of genetic linkage map and QTL analysis of net blotch resistance in barley. Int. J. Adv. Biotechnol. Res. 4, 348–363.
-
- Adee E. A. (1989). The effect of primary inoculum level of Pyrenophora tritici-repentis on tan spot epidemic development in wheat. Phytopathology 79, 873–877. 10.1094/Phyto-79-873 - DOI
-
- Afanasenko O., Mironenko N., Filatova O., Kopahnke D., Krämer I., Ordon F. (2007). Genetics of host-pathogen interactions in the Pyrenophora teres f. teres (net form)—barley (Hordeum vulgare) pathosystem. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 117, 267–280. 10.1007/s10658-006-9093-5 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

