Maternal obesity and developmental programming of neuropsychiatric disorders: An inflammatory hypothesis
- PMID: 33889757
- PMCID: PMC8040564
- DOI: 10.1177/23982128211003484
Maternal obesity and developmental programming of neuropsychiatric disorders: An inflammatory hypothesis
Abstract
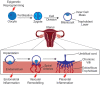
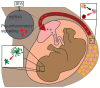
Maternal obesity is associated with the development of a variety of neuropsychiatric disorders; however, the mechanisms behind this association are not fully understood. Comparison between maternal immune activation and maternal obesity reveals similarities in associated impairments and maternal cytokine profile. Here, we present a summary of recent evidence describing how inflammatory processes contribute towards the development of neuropsychiatric disorders in the offspring of obese mothers. This includes discussion on how maternal cytokine levels, fatty acids and placental inflammation may interact with foetal neurodevelopment through changes to microglial behaviour and epigenetic modification. We also propose an exosome-mediated mechanism for the disruption of brain development under maternal obesity and discuss potential intervention strategies.
Keywords: Maternal obesity; fatty acids; inflammation; microglia; neurodevelopment; neuropsychiatric disorders; placenta.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Abuaish S, Spinieli RL, McGowan PO. (2018) Perinatal high fat diet induces early activation of endocrine stress responsivity and anxiety-like behavior in neonates. Psychoneuroendocrinology 98: 11–21. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Erviti L, Seow Y, Yin H, et al. (2011) Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nature Biotechnology 29(4): 341–345. - PubMed
-
- Amoli MM, Khatami F, Arzaghi SM, et al. (2019) Over-expression of TGF-β1 gene in medication free Schizophrenia. Psychoneuroendocrinology 99: 265–270. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

