Antihyperlipidemic and antioxidant properties of hydro-alcoholic extracts from Anogeissus leiocarpus (Combretaceae)
- PMID: 33889775
- PMCID: PMC8047486
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06648
Antihyperlipidemic and antioxidant properties of hydro-alcoholic extracts from Anogeissus leiocarpus (Combretaceae)
Abstract
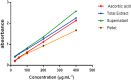
Anogeissus leiocarpus (Combretaceae) is a medicinal plant used in Togo to treat diabetes mellitus and others diseases. The present study was undertaken to evaluate the antihyperlipidemic and antioxidant activities of total extract and fractions of roots of Anogeissus leiocarpus. The antihyperlipidemic activity of the total extract and the supernatant was performed in vivo by the fructose overload test in ICR mice. Antioxidant potential was determined in vitro by methods based on scavenging of DPPH∗, total antioxidant capacity and reducing power. After the screening, phenolic compounds and flavonoids were evaluated by the well-known colorimetric assay using respectively Folin-Ciocalteu reagent and aluminium chloride. The results obtained showed that the total extract and the supernatant significantly reduced the serum and liver levels of triglycerides and hence the level of VLDL-Cholesterol compared to hyperlipidemic mice. In vitro the total extract and fractions had the ability to scavenge free radicals, to reduce metal and possessed strong total antioxidant activity. Phytochemical screening revealed the presence of polyphenols, flavonoids, alkaloids, tannins and saponosides in the extract and fractions. And the supernatant fraction contained more polyphenolic compounds than others. From this study, it is concluded that the total extract and fraction of Anogeissus leiocarpus possessed strong antihyperlipidemic, antioxidant properties and were riched in polyphenols, which can be used in the treatment of diabetes mellitus' complications. Hence, the supernatant fraction was the most biologically active.
Keywords: Anogeissus leiocarpus; Antihyperlipidemic; Antioxidant; Polyphenols; Supernatant.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- American Diabetes Association 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes-2019. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(Supplement 1):S13–S28. - PubMed
-
- Ighodaro O.M. Molecular pathways associated with oxidative stress in diabetes mellitus. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018;108:656–662. - PubMed
-
- International Diabetes Federation (IDF) ninth ed. 2019. IDF Diabetes Atlas.https://www.diabetesatlas.org/en/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

