Leptin Decreases Energy Expenditure Despite Increased Thyroid Hormone in Patients With Lipodystrophy
- PMID: 33890058
- PMCID: PMC8475236
- DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgab269
Leptin Decreases Energy Expenditure Despite Increased Thyroid Hormone in Patients With Lipodystrophy
Abstract
Context: Leptin is an adipokine that signals energy sufficiency. In rodents, leptin deficiency decreases energy expenditure (EE), which is corrected following leptin replacement. In humans, data are mixed regarding leptin-mediated effects on EE.
Objective: To determine the effects of metreleptin on EE in patients with lipodystrophy.
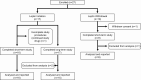
Design, setting, and patients: Nonrandomized crossover study of 25 patients with lipodystrophy (National Institutes of Health, 2013-2018).
Intervention: The initiation cohort consisted of 17 patients without prior exposure to metreleptin, studied before and after 14 days of metreleptin. The withdrawal cohort consisted of 8 previously metreleptin-treated patients, studied before and after 14 days of metreleptin withdrawal.
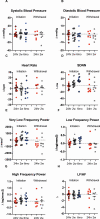
Main outcomes: 24-h total energy expenditure (TEE), resting energy expenditure (REE), autonomic nervous system activity [heart rate variability (HrV)], plasma-free triiodothyronine (T3), free thyroxine (T4), epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine.
Results: In the initiation cohort, TEE and REE decreased by 5.0% (121 ± 152 kcal/day; P = 0.006) and 5.9% (120 ± 175 kcal/day; P = 0.02). Free T3 increased by 19.4% (40 ± 49 pg/dL; P = 0.01). No changes in catecholamines or HrV were observed. In the withdrawal cohort, free T3 decreased by 8.0% (P = 0.04), free T4 decreased by 11.9% (P = 0.002), and norepinephrine decreased by 34.2% (P = 0.03), but no changes in EE, epinephrine, dopamine, or HrV were observed.
Conclusions: Metreleptin initiation decreased EE in patients with lipodystrophy, but no changes were observed after metreleptin withdrawal. Thyroid hormone was higher on metreleptin in both initiation and withdrawal cohorts. Decreased EE after metreleptin in lipodystrophy may result from reductions in energy-requiring metabolic processes that counteract increases in EE via adipose tissue-specific neuroendocrine and adrenergic signaling.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01778556.
Keywords: autonomic nervous system; energy expenditure; leptin; lipodystrophy; thyroid hormone.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society 2021.
Figures




References
-
- Friedman JM, Halaas JL. Leptin and the regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature. 1998;395(6704):763-770. - PubMed
-
- Pelleymounter MA, Cullen MJ, Baker MB, et al. . Effects of the obese gene product on body weight regulation in ob/ob mice. Science. 1995;269(5223):540-543. - PubMed
-
- Pandit R, Beerens S, Adan RAH. Role of leptin in energy expenditure: the hypothalamic perspective. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2017;312(6):R938-R947. - PubMed
-
- Montague CT, Farooqi IS, Whitehead JP, et al. . Congenital leptin deficiency is associated with severe early-onset obesity in humans. Nature. 1997;387(6636):903-908. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

