Burden of respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis on the Dutch pediatric intensive care units
- PMID: 33891158
- PMCID: PMC8429147
- DOI: 10.1007/s00431-021-04079-y
Burden of respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis on the Dutch pediatric intensive care units
Abstract
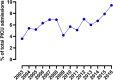
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) bronchiolitis causes substantial morbidity and mortality in young children, but insight into the burden of RSV bronchiolitis on pediatric intensive care units (PICUs) is limited. We aimed to determine the burden of RSV bronchiolitis on the PICUs in the Netherlands. Therefore, we identified all children ≤ 24 months of age with RSV bronchiolitis between 2003 and 2016 from a nationwide PICU registry. Subsequently we manually checked their patient records for correct diagnosis and collected patient characteristics, additional clinical data, respiratory support modes, and outcome. In total, 2161 children were admitted to the PICU for RSV bronchiolitis. The annual number of admissions increased significantly during the study period (β 4.05, SE 1.27, p = 0.01), and this increase was mostly driven by increased admissions in children up to 3 months old. Concomitantly, non-invasive respiratory support significantly increased (β 7.71, SE 0.92, p < 0.01), in particular the use of high flow nasal cannula (HFNC) (β 6.69, SE 0.96, p < 0.01), whereas the use of invasive ventilation remained stable.Conclusion: The burden of severe RSV bronchiolitis on PICUs has increased in the Netherlands. Concomitantly, the use of non-invasive respiratory support, especially HFNC, has increased. What is Known: • RSV bronchiolitis is a major cause of childhood morbidity and mortality and may require pediatric intensive care unit admission. • The field of pediatric critical care for severe bronchiolitis has changed due to increased non-invasive respiratory support options. What is New: • The burden of RSV bronchiolitis for the Dutch PICUs has increased. These data inform future strategic PICU resource planning and implementation of RSV preventive strategies. • There was a significant increase in the use of high flow nasal cannula at the PICU, but the use of invasive mechanical ventilation did not decrease.
Keywords: Airway management; Bronchiolitis; Child; High flow nasal cannula; Non-invasive ventilation; Respiratory syncytial viruses; Vaccination.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Shi T, McAllister DA, O'Brien KL, Simoes EAF, Madhi SA, Gessner BD, Polack FP, Balsells E, Acacio S, Aguayo C, Alassani I, Ali A, Antonio M, Awasthi S, Awori JO, Azziz-Baumgartner E, Baggett HC, Baillie VL, Balmaseda A, Barahona A, Basnet S, Bassat Q, Basualdo W, Bigogo G, Bont L, Breiman RF, Brooks WA, Broor S, Bruce N, Bruden D, Buchy P, Campbell S, Carosone-Link P, Chadha M, Chipeta J, Chou M, Clara W, Cohen C, de Cuellar E, Dang DA, Dash-Yandag B, Deloria-Knoll M, Dherani M, Eap T, Ebruke BE, Echavarria M, de Freitas Lázaro Emediato CC, Fasce RA, Feikin DR, Feng L, Gentile A, Gordon A, Goswami D, Goyet S, Groome M, Halasa N, Hirve S, Homaira N, Howie SRC, Jara J, Jroundi I, Kartasasmita CB, Khuri-Bulos N, Kotloff KL, Krishnan A, Libster R, Lopez O, Lucero MG, Lucion F, Lupisan SP, Marcone DN, McCracken J, Mejia M, Moisi JC, Montgomery JM, Moore DP, Moraleda C, Moyes J, Munywoki P, Mutyara K, Nicol MP, Nokes DJ, Nymadawa P, da Costa Oliveira MT, Oshitani H, Pandey N, Paranhos-Baccalà G, Phillips LN, Picot VS, Rahman M, Rakoto-Andrianarivelo M, Rasmussen ZA, Rath BA, Robinson A, Romero C, Russomando G, Salimi V, Sawatwong P, Scheltema N, Schweiger B, Scott JAG, Seidenberg P, Shen K, Singleton R, Sotomayor V, Strand TA, Sutanto A, Sylla M, Tapia MD, Thamthitiwat S, Thomas ED, Tokarz R, Turner C, Venter M, Waicharoen S, Wang J, Watthanaworawit W, Yoshida LM, Yu H, Zar HJ, Campbell H, Nair H, RSV Global Epidemiology Network Global, regional, and national disease burden estimates of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children in 2015: a systematic review and modelling study. Lancet. 2017;390(10098):946–958. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30938-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nair H, Nokes DJ, Gessner BD, Dherani M, Madhi SA, Singleton RJ, O'Brien KL, Roca A, Wright PF, Bruce N, Chandran A, Theodoratou E, Sutanto A, Sedyaningsih ER, Ngama M, Munywoki PK, Kartasasmita C, Simões EAF, Rudan I, Weber MW, Campbell H. Global burden of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2010;375(9725):1545–1555. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60206-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

