Network-Based Analysis of Fatal Comorbidities of COVID-19 and Potential Therapeutics
- PMID: 33891554
- PMCID: PMC8791434
- DOI: 10.1109/TCBB.2021.3075299
Network-Based Analysis of Fatal Comorbidities of COVID-19 and Potential Therapeutics
Abstract
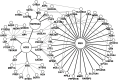
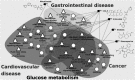
COVID-19 is a highly contagious disease caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The case-fatality rate is significantly higher in older patients and those with diabetes, cancer or cardiovascular disorders. The human proteins, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRSS2) and basigin (BSG), are involved in high-confidence host-pathogen interactions with SARS-CoV-2 proteins. We considered these three proteins as seed nodes and applied the random walk with restart method on the human interactome to construct a protein-protein interaction sub-network, which captures the effects of viral invasion. We found that 'Insulin resistance', 'AGE-RAGE signaling in diabetic complications' and 'adipocytokine signaling' were the common pathways associated with diabetes, cancer and cardiovascular disorders. The association of these critical pathways with aging and its related diseases explains the molecular basis of COVID-19 fatality. We further identified drugs that have effects on these proteins/pathways based on gene expression studies. We particularly focused on drugs that significantly downregulate ACE2 along with other critical proteins identified by the network-based approach. Among them, COL-3 had earlier shown activity against acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress, while entinostat and mocetinostat have been investigated for non-small-cell lung cancer. We propose that these drugs can be repurposed for COVID-19.
Figures

References
-
- Drosten C., et al. , “Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome,” New Engl. J. Med., vol. 348, no. 20, pp. 1967–1976, May 2003. - PubMed
-
- Zaki A. M., van Boheemen S., Bestebroer T. M., Osterhaus A. D. M. E., and Fouchier R. A. M., “Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia,” New Engl. J. Med., vol. 367, no. 19, pp. 1814–1820, Nov. 2012. - PubMed
-
- Dong L., Hu S., and Gao J., “Discovering drugs to treat coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19),” Drug Discov. Ther., vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 58–60, 2020. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

