Low immunogenicity to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination among liver transplant recipients
- PMID: 33892006
- PMCID: PMC8058047
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.04.020
Low immunogenicity to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination among liver transplant recipients
Abstract
Background & aims: Two SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines were approved to prevent COVID-19 infection, with reported vaccine efficacy of 95%. Liver transplant (LT) recipients are at risk of lower vaccine immunogenicity and were not included in the registration trials. We assessed vaccine immunogenicity and safety in this special population.
Methods: LT recipients followed at the Tel-Aviv Sourasky Medical Center and healthy volunteers were tested for SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies directed against the Spike-protein (S) and Nucleocapsid-protein (N) 10-20 days after receiving the second Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine dose. Information regarding vaccine side effects and clinical data was collected from patients and medical records.
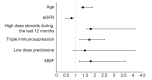
Results: Eighty LT recipients were enrolled. Mean age was 60 years and 30% were female. Twenty-five healthy volunteer controls were younger (mean age 52.7 years, p = 0.013) and mostly female (68%, p = 0.002). All participants were negative for IgG N-protein serology, indicating immunity did not result from prior COVID-19 infection. All controls were positive for IgG S-protein serology. Immunogenicity among LT recipients was significantly lower with positive serology in only 47.5% (p <0.001). Antibody titer was also significantly lower in this group (mean 95.41 AU/ml vs. 200.5 AU/ml in controls, p <0.001). Predictors for negative response among LT recipients were older age, lower estimated glomerular filtration rate, and treatment with high dose steroids and mycophenolate mofetil. No serious adverse events were reported in either group.
Conclusion: LT recipients developed substantially lower immunological response to the Pfizer-BioNTech SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-based vaccine. Factors influencing serological antibody responses include age, renal function and immunosuppressive medications. The findings require re-evaluation of vaccine regimens in this population.
Lay summary: The Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine elicited substantially inferior immunity in liver transplant recipients. Less than half of the patients developed sufficient levels of antibodies against the virus, and in those who were positive, average antibody levels were 2x less compared to healthy controls. Factors predicting non-response were older age, renal function and immunosuppressive medications.
Keywords: COVID-19; Liver transplantation; Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2; SARS-CoV-2 vaccine; vaccination.
Copyright © 2021 European Association for the Study of the Liver. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest that pertain to this work. Please refer to the accompanying ICMJE disclosure forms for further details.
Figures

Comment in
-
Protected or not protected, that is the question - First data on COVID-19 vaccine responses in patients with NAFLD and liver transplant recipients.J Hepatol. 2021 Aug;75(2):265-266. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.05.007. Epub 2021 May 25. J Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34048861 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Effectiveness of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in liver transplanted patients: The debate is open!J Hepatol. 2022 Jan;76(1):237-239. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.07.034. Epub 2021 Aug 3. J Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 34358567 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Clinical update on the efficacy of anti-SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines in patients on the waiting list for liver transplantation and in liver transplant recipients.Dig Liver Dis. 2021 Oct;53(10):1232-1234. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2021.07.019. Epub 2021 Jul 29. Dig Liver Dis. 2021. PMID: 34393073 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- American Society of Transplantation: COVID-19: VACCINE FAQ SHEET. https://www.myast.org/covid-19-vaccine-faq-sheet. Last entered 24/03/2021.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

