GARFIELD-AF risk score for mortality, stroke, and bleeding within 2 years in patients with atrial fibrillation
- PMID: 33892489
- PMCID: PMC8888127
- DOI: 10.1093/ehjqcco/qcab028
GARFIELD-AF risk score for mortality, stroke, and bleeding within 2 years in patients with atrial fibrillation
Abstract
Aims: To determine whether the Global Anticoagulant Registry in the FIELD-Atrial Fibrillation (GARFIELD-AF) integrated risk tool predicts mortality, non-haemorrhagic stroke/systemic embolism, and major bleeding for up to 2 years after new-onset AF and to assess how this risk tool performs compared with CHA2DS2-VASc and HAS-BLED.
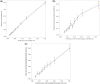
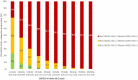
Methods and results: Potential predictors of events included demographic and clinical characteristics, choice of treatment, and lifestyle factors. A Cox proportional hazards model was identified for each outcome by least absolute shrinkage and selection operator methods. Indices were evaluated in comparison with CHA2DS2-VASc and HAS-BLED risk predictors. Models were validated internally and externally in ORBIT-AF and Danish nationwide registries. Among the 52 080 patients enrolled in GARFIELD-AF, 52 032 had follow-up data. The GARFIELD-AF risk tool outperformed CHA2DS2-VASc for all-cause mortality in all cohorts. The GARFIELD-AF risk score was superior to CHA2DS2-VASc for non-haemorrhagic stroke, and it outperformed HAS-BLED for major bleeding in internal validation and in the Danish AF cohort. In very low- to low-risk patients [CHA2DS2-VASc 0 or 1 (men) and 1 or 2 (women)], the GARFIELD-AF risk score offered strong discriminatory value for all the endpoints when compared to CHA2DS2-VASc and HAS-BLED. The GARFIELD-AF tool also included the effect of oral anticoagulation (OAC) therapy, thus allowing clinicians to compare the expected outcome of different anticoagulant treatment decisions [i.e. no OAC, non-vitamin K antagonist (VKA) oral anticoagulants, or VKAs].
Conclusions: The GARFIELD-AF risk tool outperformed CHA2DS2-VASc at predicting death and non-haemorrhagic stroke, and it outperformed HAS-BLED for major bleeding in overall as well as in very low- to low-risk group patients with AF.
Clinical trial registration: URL: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Unique identifier for GARFIELD-AF: NCT01090362, ORBIT-AF I: NCT01165710; ORBIT-AF II: NCT01701817.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; CHA2DS2-VASc; Risk stratification; GARFIELD-AF.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Improved risk stratification of patients with atrial fibrillation: an integrated GARFIELD-AF tool for the prediction of mortality, stroke and bleed in patients with and without anticoagulation.BMJ Open. 2017 Dec 21;7(12):e017157. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-017157. BMJ Open. 2017. PMID: 29273652 Free PMC article.
-
Atrial fibrillation outcomes in patients from Asia and non-Asia countries: insights from GARFIELD-AF.Open Heart. 2025 Feb 6;12(1):e003109. doi: 10.1136/openhrt-2024-003109. Open Heart. 2025. PMID: 39914996 Free PMC article.
-
Stroke-bleeding risk score pairings within individuals in the outcomes registry for better informed treatment of atrial fibrillation (ORBIT-AF) registry.Int J Cardiol. 2025 Feb 15;421:132912. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2024.132912. Epub 2024 Dec 19. Int J Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 39708904
-
Ischemic stroke risk in East Asian patients with CHA2DS2-VASc score of 1: systematic review and meta-analysis.Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2017 Feb;15(2):145-150. doi: 10.1080/14779072.2017.1281742. Epub 2017 Jan 20. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2017. PMID: 28076988
-
Factor Xa inhibitors versus vitamin K antagonists for preventing cerebral or systemic embolism in patients with atrial fibrillation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Aug 8;(8):CD008980. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008980.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Mar 06;3:CD008980. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008980.pub3. PMID: 23925867 Updated.
Cited by
-
Universal Clinician Device for improving risk prediction and management of patients with atrial fibrillation: an assumed benefit analysis.Eur Heart J Digit Health. 2022 Mar 25;3(2):181-194. doi: 10.1093/ehjdh/ztac011. eCollection 2022 Jun. Eur Heart J Digit Health. 2022. PMID: 36713019 Free PMC article.
-
The Risk of Atrial Fibrillation and Previous Ischemic Stroke in Cognitive Decline.J Clin Med. 2024 Jul 14;13(14):4117. doi: 10.3390/jcm13144117. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39064156 Free PMC article.
-
Anticoagulation Patterns in Ischemic Stroke Patients with Atrial Fibrillation in Developing Country: Insights from the Stroke Registry in Vietnam.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024 Aug 30;11(9):269. doi: 10.3390/jcdd11090269. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024. PMID: 39330327 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of bleeding risk scores and evaluation of major bleeding predictive factors in patients with major bleeding due to vitamin K antagonist use.Heliyon. 2023 Aug 12;9(8):e19079. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19079. eCollection 2023 Aug. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37636426 Free PMC article.
-
Optimising prediction of mortality, stroke, and major bleeding for patients with atrial fibrillation: validation of the GARFIELD-AF tool in UK primary care electronic records.Br J Gen Pract. 2023 Oct 26;73(736):e816-e824. doi: 10.3399/BJGP.2023.0082. Print 2023 Nov. Br J Gen Pract. 2023. PMID: 37845083 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wolf PA, Abbott RD, Kannel WB.. Atrial fibrillation as an independent risk factor for stroke: the Framingham Study. Stroke 1991;22:983–988. - PubMed
-
- Odutayo A, Wong CX, Hsiao AJ, Hopewell S, Altman DG, Emdin CA.. Atrial fibrillation and risks of cardiovascular disease, renal disease, and death: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2016;354:i4482. - PubMed
-
- Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, Arbelo E, Bax JJ, Blomström-Lundqvist C. et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): the Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J 2021;42:373–498. - PubMed
-
- Fox KAA, Lucas JE, Pieper KS, Bassand J-P, Camm AJ, Fitzmaurice DA. et al.; GARFIELD-AF Investigators. Improved risk stratification of patients with atrial fibrillation: an integrated GARFIELD-AF tool for the prediction of mortality, stroke and bleed in patients with and without anticoagulation. BMJ Open 2017;7:e017157. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

