Homozygous variant p. Arg90His in NCF1 is associated with early-onset Interferonopathy: a case report
- PMID: 33892719
- PMCID: PMC8063424
- DOI: 10.1186/s12969-021-00536-y
Homozygous variant p. Arg90His in NCF1 is associated with early-onset Interferonopathy: a case report
Abstract
Background: Biallelic loss-of-function variants in NCF1 lead to reactive oxygen species deficiency and chronic granulomatous disease (CGD). Heterozygosity for the p.Arg90His variant in NCF1 has been associated with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and Sjögren's syndrome in adult patients. This study demonstrates the association of the homozygous p.Arg90His variant with interferonopathy with features of autoinflammation and autoimmunity in a pediatric patient.
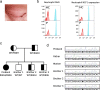
Case presentation: A 5-year old female of Indian ancestry with early-onset recurrent fever and headache, and persistently elevated antinuclear, anti-Ro, and anti-La antibodies was found to carry the homozygous p.Arg90His variant in NCF1 through exome sequencing. Her unaffected parents and three other siblings were carriers for the mutant allele. Because the presence of two NCF1 pseudogenes, this variant was confirmed by independent genotyping methods. Her intracellular neutrophil oxidative burst and NCF1 expression levels were normal, and no clinical features of CGD were apparent. Gene expression analysis in peripheral blood detected an interferon gene expression signature, which was further supported by cytokine analyses of supernatants of cultured patient's cells. These findings suggested that her inflammatory disease is at least in part mediated by type I interferons. While her fever episodes responded well to systemic steroids, treatment with the JAK inhibitor tofacitinib resulted in decreased serum ferritin levels and reduced frequency of fevers.
Conclusion: Homozygosity for p.Arg90His in NCF1 should be considered contributory in young patients with an atypical systemic inflammatory antecedent phenotype that may evolve into autoimmunity later in life. The complex genomic organization of NCF1 poses a difficulty for high-throughput genotyping techniques and variants in this gene should be carefully evaluated when using the next generation and Sanger sequencing technologies. The p.Arg90His variant is found at a variable allele frequency in different populations, and is higher in people of South East Asian ancestry. In complex genetic diseases such as SLE, other rare and common susceptibility alleles might be necessary for the full disease expressivity.
Keywords: Autoimmunity; Autoinflammation; Interferons; NCF1; Systemic lupus erythematosus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest
Figures

Comment in
-
Comment on: homozygous variant p. Arg90His in NCF1 is associated with early-onset interferonopathy: a case report.Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2021 Aug 16;19(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s12969-021-00612-3. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2021. PMID: 34399789 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
A missense variant in NCF1 is associated with susceptibility to multiple autoimmune diseases.Nat Genet. 2017 Mar;49(3):433-437. doi: 10.1038/ng.3782. Epub 2017 Jan 30. Nat Genet. 2017. PMID: 28135245 Free PMC article.
-
Association of NCF1 polymorphism with systemic lupus erythematosus and systemic sclerosis but not with ANCA-associated vasculitis in a Japanese population.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 8;9(1):16366. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-52920-0. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31705128 Free PMC article.
-
Human SLE variant NCF1-R90H promotes kidney damage and murine lupus through enhanced Tfh2 responses induced by defective efferocytosis of macrophages.Ann Rheum Dis. 2022 Feb;81(2):255-267. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-220793. Epub 2021 Sep 23. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022. PMID: 34556485
-
Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of the Association between a Hypoactive NCF1 Variant and Various Autoimmune Diseases.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Aug 16;11(8):1589. doi: 10.3390/antiox11081589. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36009308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low Production of Reactive Oxygen Species Drives Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Trends Mol Med. 2019 Oct;25(10):826-835. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2019.06.001. Epub 2019 Jul 11. Trends Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31303528 Review.
Cited by
-
Comment on: homozygous variant p. Arg90His in NCF1 is associated with early-onset interferonopathy: a case report.Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2021 Aug 16;19(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s12969-021-00612-3. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2021. PMID: 34399789 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus genetics: insights into pathogenesis and implications for therapy.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2024 Oct;20(10):635-648. doi: 10.1038/s41584-024-01152-2. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 39232240 Review.
-
Targeted RNAseq Improves Clinical Diagnosis of Very Early-Onset Pediatric Immune Dysregulation.J Pers Med. 2022 Jun 1;12(6):919. doi: 10.3390/jpm12060919. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35743704 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhao J, Ma J, Deng Y, Kelly JA, Kim K, Bang SY, Lee HS, Li QZ, Wakeland EK, Qiu R, Liu M, Guo J, Li Z, Tan W, Rasmussen A, Lessard CJ, Sivils KL, Hahn BH, Grossman JM, Kamen DL, Gilkeson GS, Bae SC, Gaffney PM, Shen N, Tsao BP. A missense variant in NCF1 is associated with susceptibility to multiple autoimmune diseases. Nat Genet. 2017;49(3):433–437. doi: 10.1038/ng.3782. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Olsson LM, Johansson AC, Gullstrand B, Jonsen A, Saevarsdottir S, Ronnblom L, et al. A single nucleotide polymorphism in the NCF1 gene leading to reduced oxidative burst is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(9):1607–1613. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211287. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

