MAPK-Activated Transcription Factor PxJun Suppresses PxABCB1 Expression and Confers Resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac Toxin in Plutella xylostella (L.)
- PMID: 33893113
- PMCID: PMC8315950
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00466-21
MAPK-Activated Transcription Factor PxJun Suppresses PxABCB1 Expression and Confers Resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac Toxin in Plutella xylostella (L.)
Abstract
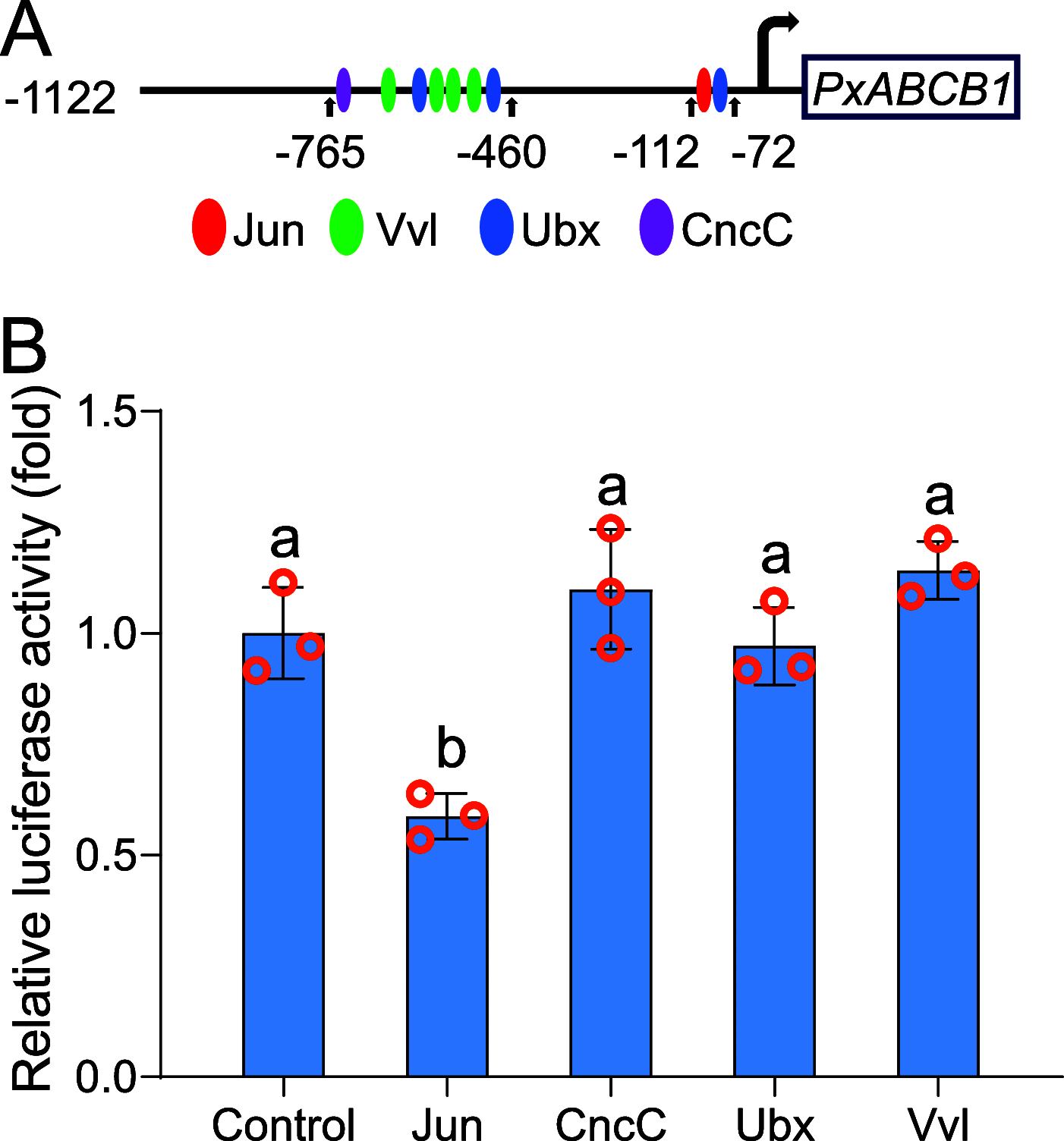
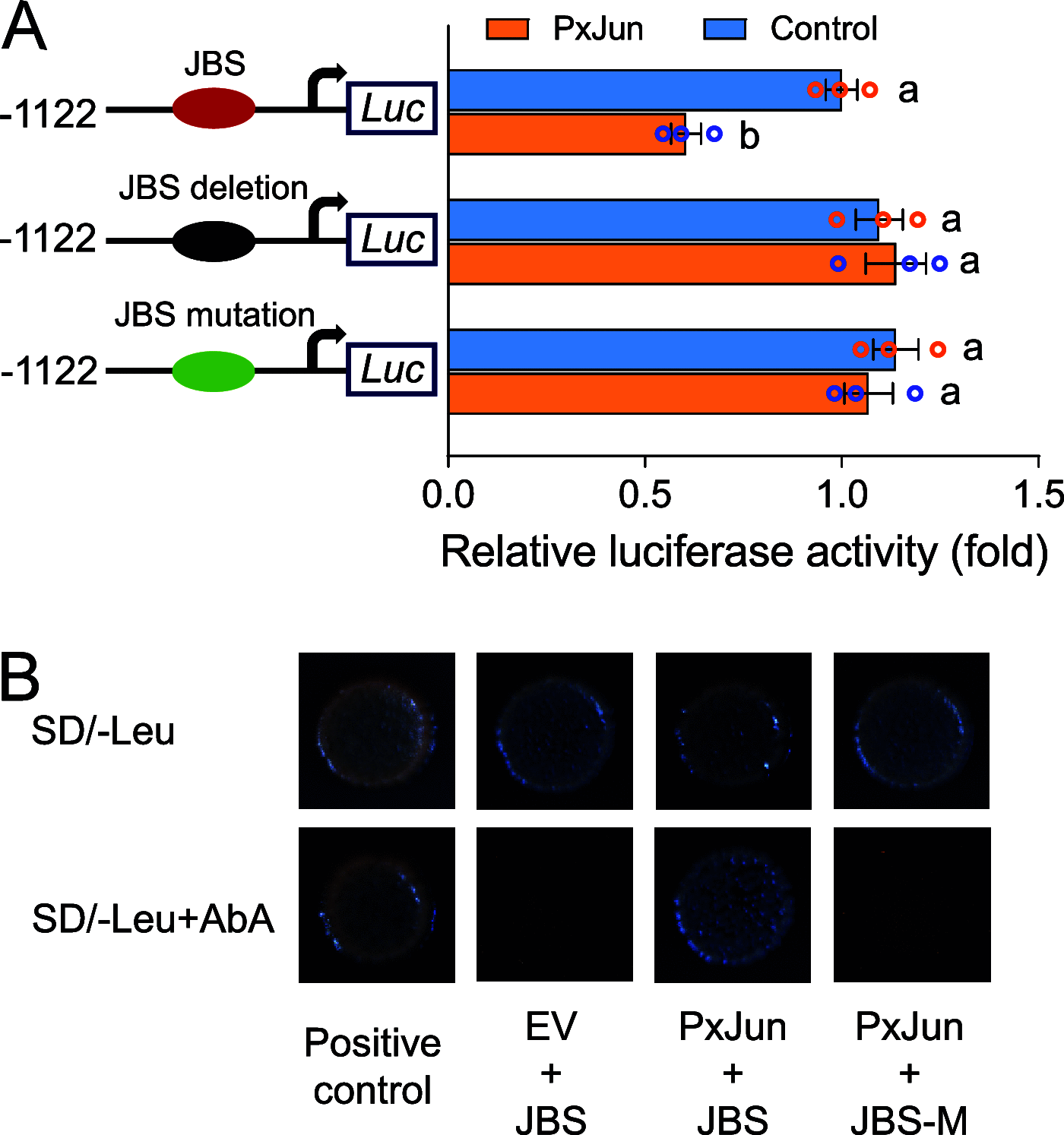
Deciphering the molecular mechanisms underlying insect resistance to Cry toxins produced by Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) is pivotal for the sustainable utilization of Bt biopesticides and transgenic Bt crops. Previously, we identified that mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)-mediated reduced expression of the PxABCB1 gene is associated with Bt Cry1Ac resistance in the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (L.). However, the underlying transcriptional regulation mechanism remains enigmatic. Here, the PxABCB1 promoter in Cry1Ac-susceptible and Cry1Ac-resistant P. xylostella strains was cloned and analyzed and found to contain a putative Jun binding site (JBS). A dual-luciferase reporter assay and yeast one-hybrid assay demonstrated that the transcription factor PxJun repressed PxABCB1 expression by interacting with this JBS. The expression levels of PxJun were increased in the midguts of all resistant strains compared to the susceptible strain. Silencing of PxJun expression significantly elevated PxABCB1 expression and Cry1Ac susceptibility in the resistant NIL-R strain, and silencing of PxMAP4K4 expression decreased PxJun expression and also increased PxABCB1 expression. These results indicate that MAPK-activated PxJun suppresses PxABCB1 expression to confer Cry1Ac resistance in P. xylostella, deepening our understanding of the transcriptional regulation of midgut Cry receptor genes and the molecular basis of insect resistance to Bt Cry toxins. IMPORTANCE The transcriptional regulation mechanisms underlying reduced expression of Bt toxin receptor genes in Bt-resistant insects remain elusive. This study unveils that a transcription factor PxJun activated by the MAPK signaling pathway represses PxABCB1 expression and confers Cry1Ac resistance in P. xylostella. Our results provide new insights into the transcriptional regulation mechanisms of midgut Cry receptor genes and deepen our understanding of the molecular basis of insect resistance to Bt Cry toxins. To our knowledge, this study identified the first transcription factor that can be involved in the transcriptional regulation mechanisms of midgut Cry receptor genes in Bt-resistant insects.
Keywords: ABCB1; Bacillus thuringiensis; Cry1Ac resistance; Jun; Plutella xylostella; transcription factor.
Figures







Similar articles
-
MAP4K4 controlled transcription factor POUM1 regulates PxABCG1 expression influencing Cry1Ac resistance in Plutella xylostella (L.).Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2022 Mar;182:105053. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2022.105053. Epub 2022 Feb 7. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35249643
-
Reduced expression of the P-glycoprotein gene PxABCB1 is linked to resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac toxin in Plutella xylostella (L.).Pest Manag Sci. 2020 Feb;76(2):712-720. doi: 10.1002/ps.5569. Epub 2019 Aug 29. Pest Manag Sci. 2020. PMID: 31359575
-
MAPK-mediated transcription factor GATAd contributes to Cry1Ac resistance in diamondback moth by reducing PxmALP expression.PLoS Genet. 2022 Feb 3;18(2):e1010037. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010037. eCollection 2022 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2022. PMID: 35113858 Free PMC article.
-
Utilization of Diverse Molecules as Receptors by Cry Toxin and the Promiscuous Nature of Receptor-Binding Sites Which Accounts for the Diversity.Biomolecules. 2024 Apr 1;14(4):425. doi: 10.3390/biom14040425. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38672442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signaling versus punching hole: How do Bacillus thuringiensis toxins kill insect midgut cells?Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009 Apr;66(8):1337-49. doi: 10.1007/s00018-008-8330-9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009. PMID: 19132293 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Potential Role of the Methionine Aminopeptidase Gene PxMetAP1 in a Cosmopolitan Pest for Bacillus thuringiensis Toxin Tolerance.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 27;23(21):13005. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113005. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361800 Free PMC article.
-
Novel genetic basis of resistance to Bt toxin Cry1Ac in Helicoverpa zea.Genetics. 2022 May 5;221(1):iyac037. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyac037. Genetics. 2022. PMID: 35234875 Free PMC article.
-
A cis-Acting Mutation in the PxABCG1 Promoter Is Associated with Cry1Ac Resistance in Plutella xylostella (L.).Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 5;22(11):6106. doi: 10.3390/ijms22116106. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34198929 Free PMC article.
-
A midgut transcriptional regulatory loop favors an insect host to withstand a bacterial pathogen.Innovation (Camb). 2024 Jul 25;5(5):100675. doi: 10.1016/j.xinn.2024.100675. eCollection 2024 Sep 9. Innovation (Camb). 2024. PMID: 39170942 Free PMC article.
-
A single transcription factor facilitates an insect host combating Bacillus thuringiensis infection while maintaining fitness.Nat Commun. 2022 Oct 12;13(1):6024. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33706-x. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36224245 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sanchis V. 2011. From microbial sprays to insect-resistant transgenic plants: history of the biopesticide Bacillus thuringiensis: a review. Agron Sustain Dev 31:217–231. 10.1051/agro/2010027. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

