CRISPR-based genome editing in primary human pancreatic islet cells
- PMID: 33893274
- PMCID: PMC8065166
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-22651-w
CRISPR-based genome editing in primary human pancreatic islet cells
Abstract
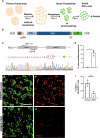
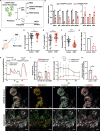
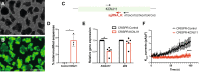
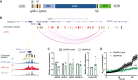
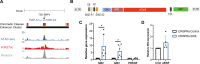
Gene targeting studies in primary human islets could advance our understanding of mechanisms driving diabetes pathogenesis. Here, we demonstrate successful genome editing in primary human islets using clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) and CRISPR-associated protein 9 (Cas9). CRISPR-based targeting efficiently mutated protein-coding exons, resulting in acute loss of islet β-cell regulators, like the transcription factor PDX1 and the KATP channel subunit KIR6.2, accompanied by impaired β-cell regulation and function. CRISPR targeting of non-coding DNA harboring type 2 diabetes (T2D) risk variants revealed changes in ABCC8, SIX2 and SIX3 expression, and impaired β-cell function, thereby linking regulatory elements in these target genes to T2D genetic susceptibility. Advances here establish a paradigm for genetic studies in human islet cells, and reveal regulatory and genetic mechanisms linking non-coding variants to human diabetes risk.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

