COVID-19 pathophysiology may be driven by an imbalance in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
- PMID: 33893295
- PMCID: PMC8065208
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-22713-z
COVID-19 pathophysiology may be driven by an imbalance in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
Abstract
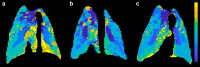
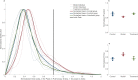
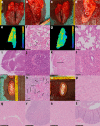
SARS-CoV-2 uses ACE2, an inhibitor of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS), for cellular entry. Studies indicate that RAAS imbalance worsens the prognosis in COVID-19. We present a consecutive retrospective COVID-19 cohort with findings of frequent pulmonary thromboembolism (17%), high pulmonary artery pressure (60%) and lung MRI perfusion disturbances. We demonstrate, in swine, that infusing angiotensin II or blocking ACE2 induces increased pulmonary artery pressure, reduces blood oxygenation, increases coagulation, disturbs lung perfusion, induces diffuse alveolar damage, and acute tubular necrosis compared to control animals. We further demonstrate that this imbalanced state can be ameliorated by infusion of an angiotensin receptor blocker and low-molecular-weight heparin. In this work, we show that a pathophysiological state in swine induced by RAAS imbalance shares several features with the clinical COVID-19 presentation. Therefore, we propose that severe COVID-19 could partially be driven by a RAAS imbalance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
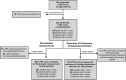
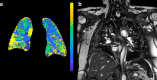
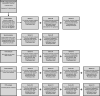
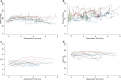

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

