Forecasting the dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes across bacterial genomes
- PMID: 33893312
- PMCID: PMC8065159
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-22757-1
Forecasting the dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes across bacterial genomes
Abstract
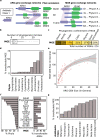
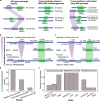
Antibiotic resistance spreads among bacteria through horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs). Here, we set out to determine predictive features of ARG transfer among bacterial clades. We use a statistical framework to identify putative horizontally transferred ARGs and the groups of bacteria that disseminate them. We identify 152 gene exchange networks containing 22,963 bacterial genomes. Analysis of ARG-surrounding sequences identify genes encoding putative mobilisation elements such as transposases and integrases that may be involved in gene transfer between genomes. Certain ARGs appear to be frequently mobilised by different mobile genetic elements. We characterise the phylogenetic reach of these mobilisation elements to predict the potential future dissemination of known ARGs. Using a separate database with 472,798 genomes from Streptococcaceae, Staphylococcaceae and Enterobacteriaceae, we confirm 34 of 94 predicted mobilisations. We explore transfer barriers beyond mobilisation and show experimentally that physiological constraints of the host can explain why specific genes are largely confined to Gram-negative bacteria although their mobile elements support dissemination to Gram-positive bacteria. Our approach may potentially enable better risk assessment of future resistance gene dissemination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Sommer, M. O., Munck, C., Toft-Kehler, R. V. & Andersson, D. I. Prediction of antibiotic resistance: time for a new preclinical paradigm? Nat. Rev. Microbiol.15, 689–696 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Hamilton, W. L. & Wenlock, R. Antimicrobial resistance: a major threat to public health. Camb. Med. J.10.7244/cmj (2016).
-
- Allen, H. K. et al. Call of the wild: antibiotic resistance genes in natural environments. Nat. Rev. Microbiol.8, 251–259 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Martínez, J. L. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in natural environments. Science321, 365–367 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

