Synthetic high-density lipoprotein nanoparticles: Good things in small packages
- PMID: 33894397
- PMCID: PMC8328934
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtos.2021.03.001
Synthetic high-density lipoprotein nanoparticles: Good things in small packages
Abstract
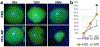
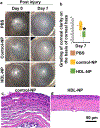
Medicine has been a great beneficiary of the nanotechnology revolution. Nanotechnology involves the synthesis of functional materials with at least one size dimension between 1 and 100 nm. Advances in the field have enabled the synthesis of bio-nanoparticles that can interface with physiological systems to modulate fundamental cellular processes. One example of a diverse acting nanoparticle-based therapeutic is synthetic high-density lipoprotein (HDL) nanoparticles (NP), which have great potential for treating diseases of the ocular surface. Our group has developed a spherical HDL NP using a gold nanoparticle core. HDL NPs: (i) closely mimic the physical and chemical features of natural HDLs; (ii) contain apoA-I; (iii) bind with high-affinity to SR-B1, which is the major receptor through which HDL modulates cell cholesterol metabolism and controls the selective uptake of HDL cargo into cells; (iv) are non-toxic to cells and tissues; and (v) can be chemically engineered to display nearly any surface or core composition desired. With respect to the ocular surface, topical application of HDL NPs accelerates re-epithelization of the cornea following wounding, attenuates inflammation resulting from chemical burns and/or other stresses, and effectively delivers microRNAs with biological activity to corneal cells and tissues. HDL NPs will be the foundation of a new class of topical eye drops with great translational potential and exemplify the impact that nanoparticles can have in medicine.
Keywords: Chemical burn; Cholesterol; Cornea; Eye drop; Inflammation; Lipoprotein; Nanotechnology; Wound healing; microRNA.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Feynman RP. There's plenty of room at the bottom. Eng Sci. 1960;23:22–36.
-
- Taniguchi N, Arakawa C, Kobayashi T. On the basic concept of nano-technology. Proceedings of the International Conference on Production Engineering. Tokyo, Japan1974. p. 26–9.
-
- Vert M, Doi Y, Hellwich K-H, Hess M, Hodge P, Kubisa P, et al. Terminology for biorelated polymers and applications (IUPAC Recommendations 2012). Pure Appl Chem. 2012;84:377–410.
-
- Lepeltier E, Rijo P, Rizzolio F, Popovtzer R, Petrikaite V, Assaraf YG, et al. Nanomedicine to target multidrug resistant tumors. Drug Resist Updat. 2020;52:100704. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

