Eight-month follow-up of olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions in recovered COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 33894627
- PMCID: PMC8055924
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2021.103065
Eight-month follow-up of olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions in recovered COVID-19 patients
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the recovery of loss of smell and taste among recovered COVID-19 patients.
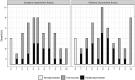
Materials and methods: This cross-sectional follow-up study is a sequel to a study by Biadsee et al. Among the previous study population of 128 non-hospitalized patients, positive for COVID-19 by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), 97 patients participated in a survey designed for this study. Information and data regarding loss of smell and taste, rate of recovery, xerostomia, and additional symptoms; (Cough, Myalgia, Weakness, Rhinorrhea, Nasal congestion) were collected.
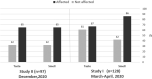
Results: A total of 43 men and 54 women were included. Mean age was 37.5 years (range 19-74). Mean follow-up was 229 days (range 191-253). Sixty-five patients reported gustatory dysfunction during the disease of which 61.5% reported full recovery, 38.5% partial recovery. Of 65 patients who reported olfactory impairment during the disease, 52% had full recovery and 48% reported partial recovery of olfactory function. Complete recovery of olfactory function was positively associated with full recovery of gustatory function (p = 0.01). Gender did not significantly affect the recovery of OD and GD (p = 0.45, p = 0.90, respectively). Patients who experienced olfactory dysfunction as an initial symptom had lower rates of olfactory complete recovery (p = 0.043).
Conclusion: After a mean follow-up of 229 days, complete recovery of smell and taste functions occurred in 52% and 61.5%, respectively. However, dysfunction persisted in 48%-38.5% of patients.
Keywords: COVID-19 recovery; Gustatory dysfunction; Olfactory dysfunction; Post-viral olfactory function loss; Xerostomia.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Comment in
-
The study of recovery rates of COVID-19 olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions requires psychophysical evaluations.Am J Otolaryngol. 2021 Nov-Dec;42(6):103168. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2021.103168. Epub 2021 Jul 29. Am J Otolaryngol. 2021. PMID: 34339959 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Chary E., Carsuzaa F., Trijolet J.-P., Capitaine A.-L., Roncato-Saberan M., Fouet K., et al. Prevalence and recovery from olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions in covid-19 infection: a prospective multicenter study. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2020;34:686–693. doi: 10.1177/1945892420930954. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

