Antireflux endoscopic injection therapy in post-pubertal patients via techniques adopted for the dilated ureteral orifice: a retrospective single-center study
- PMID: 33894751
- PMCID: PMC8067324
- DOI: 10.1186/s12894-021-00842-3
Antireflux endoscopic injection therapy in post-pubertal patients via techniques adopted for the dilated ureteral orifice: a retrospective single-center study
Abstract
Background: To investigate the efficacy and safety of endoscopic injection therapy for vesicoureteral reflux in post-pubertal patients with dilated ureteral orifice via modified hydrodistension implantation techniques.
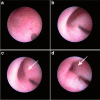
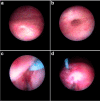
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed medical records including operational procedure and clinical course of all consecutive patients over 12 years old with a history of injection therapy. Endoscopic injection of dextranomer/hyaluronic acid copolymer was performed under hydrodistension implantation technique with some modifications in order to inject through dilated ureteral orifice align with the intramural ureter. Technical selections were done according to hydrodistension grade of the ureteral orifice. Voiding cystourethrography was evaluated at 3 months postoperatively. Hydronephrosis was evaluated using ultrasonography preoperatively until 6 months postoperatively.
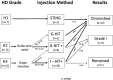
Results: From 2016 to 2019, 12 patients (all female, 16 ureteral units; median age 32 [range 15-61] years) underwent endoscopic injection therapy at one of our institutions. We have identified grade II vesicoureteral reflux in 5 ureters, grade III in 8, and grade IV in 3 ureters. Grade 3 ureteral-orifice dilation were presented in 12 ureters (75%), grade 2 in 3 and grade 1 in 1 ureter in the present cases. Postoperatively, vesicoureteral reflux was diminished to grade 0 in 12 ureteral units (75%), decreased to grade I in 3 (9%), and remained grade III in 1 (6%). Three patients reported dull flank pain for several days postoperatively and there was 1 case of acute pyelonephritis. Temporary hydronephrosis was confirmed in 3 ureteral units (19%) at 1 month postoperatively. Median follow-up duration was 23 (range 13-63) months long. Although, 3 patients were experienced f-UTI 1-2 times, repeated VCUG showed no VUR recurrence.
Conclusions: According to hydrodistension grade of the ureteral orifice, endoscopic injection therapy via modified hydrodistension implantation technique is an effective and safe treatment for vesicoureteral reflux in post-pubertal female patients with dilated ureteral orifice. While ureteral deformities or a history of anti-reflux surgery may increase the risks, these can be managed with appropriate methods that ensure sufficient mound appearance and height.
Keywords: Dextranomer/hyaluronic acid copolymer; HIT; STING; Urinary tract infection; Vesicoureteral reflux.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Antoine EK, Darius JB. Management strategies for vesicoureteral reflux. In: Partin AW, editor. Campbell-Walsh-Wein Urology. 12. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2020. p. 490.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

