Carriage of upper respiratory tract pathogens in rural communities of Sarawak, Malaysian Borneo
- PMID: 33894778
- PMCID: PMC8070298
- DOI: 10.1186/s41479-021-00084-9
Carriage of upper respiratory tract pathogens in rural communities of Sarawak, Malaysian Borneo
Abstract
Introduction: Pneumonia is a leading cause of death in Malaysia. Whilst many studies have reported the aetiology of pneumonia in Western countries, the epidemiology of pneumonia in Malaysia remains poorly understood. As carriage is a prerequisite for disease, we sought to improve our understanding of the carriage and antimicrobial resistance (AMR) of respiratory tract pathogens in Malaysia. The rural communities of Sarawak are an understudied part of the Malaysian population and were the focus of this study, allowing us to gain a better understanding of bacterial epidemiology in this population.
Methods: A population-based survey of bacterial carriage was undertaken in participants of all ages from rural communities in Sarawak, Malaysia. Nasopharyngeal, nasal, mouth and oropharyngeal swabs were taken. Bacteria were isolated from each swab and identified by culture-based methods and antimicrobial susceptibility testing conducted by disk diffusion or E test.
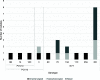
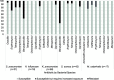
Results: 140 participants were recruited from five rural communities. Klebsiella pneumoniae was most commonly isolated from participants (30.0%), followed by Staphylococcus aureus (20.7%), Streptococcus pneumoniae (10.7%), Haemophilus influenzae (9.3%), Moraxella catarrhalis (6.4%), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (6.4%) and Neisseria meningitidis (5.0%). Of the 21 S. pneumoniae isolated, 33.3 and 14.3% were serotypes included in the 13 valent PCV (PCV13) and 10 valent PCV (PCV10) respectively. 33.8% of all species were resistant to at least one antibiotic, however all bacterial species except S. pneumoniae were susceptible to at least one type of antibiotic.
Conclusion: To our knowledge, this is the first bacterial carriage study undertaken in East Malaysia. We provide valuable and timely data regarding the epidemiology and AMR of respiratory pathogens commonly associated with pneumonia. Further surveillance in Malaysia is necessary to monitor changes in the carriage prevalence of upper respiratory tract pathogens and the emergence of AMR, particularly as PCV is added to the National Immunisation Programme (NIP).
Keywords: AMR; Carriage; Malaysia; Pathogen; Pneumonia; Respiratory.
Conflict of interest statement
SCC acts as principal investigator on studies conducted on behalf of University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust/University of Southampton that are sponsored by vaccine manufacturers but receives no personal payments from them. SCC has participated in advisory boards for vaccine manufacturers but receives no personal payments for this work. SCC has received financial assistance from vaccine manufacturers to attend conferences. DWC was a post-doctoral researcher on projects funded by Pfizer and GSK between April 2014 and October 2017. All grants and honoraria are paid into accounts within the respective NHS Trusts or Universities, or to independent charities. All other authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Global Burden of Disease 2016 Causes of Death Collaborators Global, regional, and national age-sex specific mortality for 264 causes of death, 1980–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017;390(10100):1151–1210. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32152-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Statistics on Causes of Death, Malaysia, 2018 [press release]. Malaysia: Department of Statistics Malaysia, 31st October 2018 2018.
-
- Garcia-Vidal C, Fernandez-Sabe N, Carratala J, Diaz V, Verdaguer R, Dorca J, et al. Early mortality in patients with community-acquired pneumonia: causes and risk factors. Eur Respir J. 2008;32(3):733–9. 10.1183/09031936.00128107. - PubMed
-
- Limper AH. 97 - overview of pneumonia. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, editors. Goldman's Cecil medicine (twenty Fourth Edition) Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders; 2012. pp. 587–596.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

