Myosin 7b is a regulatory long noncoding RNA (lncMYH7b) in the human heart
- PMID: 33895132
- PMCID: PMC8141895
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100694
Myosin 7b is a regulatory long noncoding RNA (lncMYH7b) in the human heart
Abstract
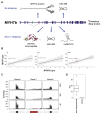
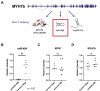
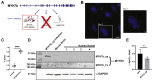
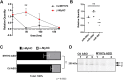
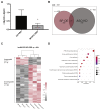
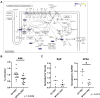
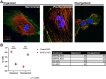
Myosin heavy chain 7b (MYH7b) is an ancient member of the myosin heavy chain motor protein family that is expressed in striated muscles. In mammalian cardiac muscle, MYH7b RNA is expressed along with two other myosin heavy chains, β-myosin heavy chain (β-MyHC) and α-myosin heavy chain (α-MyHC). However, unlike β-MyHC and α-MyHC, which are maintained in a careful balance at the protein level, the MYH7b locus does not produce a full-length protein in the heart due to a posttranscriptional exon-skipping mechanism that occurs in a tissue-specific manner. Whether this locus has a role in the heart beyond producing its intronic microRNA, miR-499, was unclear. Using cardiomyocytes derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells as a model system, we found that the noncoding exon-skipped RNA (lncMYH7b) affects the transcriptional landscape of human cardiomyocytes, independent of miR-499. Specifically, lncMYH7b regulates the ratio of β-MyHC to α-MyHC, which is crucial for cardiac contractility. We also found that lncMYH7b regulates beat rate and sarcomere formation in cardiomyocytes. This regulation is likely achieved through control of a member of the TEA domain transcription factor family (TEAD3, which is known to regulate β-MyHC). Therefore, we conclude that this ancient gene has been repurposed by alternative splicing to produce a regulatory long-noncoding RNA in the human heart that affects cardiac myosin composition.
Keywords: alternative splicing; gene regulation; heart failure; long noncoding RNA (lncRNA); myosin heavy chain (MyHC); myosin heavy chain 7b (MYH7b).
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest No conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures
References
-
- Weiss A., Leinwand L. The mammalian myosin heavy chain gene family. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1996;12:417–439. - PubMed
-
- Miyata S., Minobe W., Bristow M.R., Leinwand L.A. Myosin heavy chain isoform expression in the failing and nonfailing human heart. Circ. Res. 2000;86:386–390. - PubMed
-
- Lowes B.D., Gilbert E.M., Abraham W.T., Minobe W.A., Larrabee P., Ferguson D., Wolfel E.E., Lindenfeld J.A., Tsvetkova T., Robertson A.D., Quaife R.A., Bristow M.R. Myocardial gene expression in dilated cardiomyopathy treated with beta-blocking agents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002;346:1357–1365. - PubMed
-
- Hasegawa K., Lee S.J., Jobe S.M., Markham B.E., Kitsis R.N. cis-Acting sequences that mediate induction of beta-myosin heavy chain gene expression during left ventricular hypertrophy due to aortic constriction. Circulation. 1997;96:3943–3953. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

