Evidence in primates supporting the use of chemogenetics for the treatment of human refractory neuropsychiatric disorders
- PMID: 33895327
- PMCID: PMC8636156
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.04.021
Evidence in primates supporting the use of chemogenetics for the treatment of human refractory neuropsychiatric disorders
Abstract
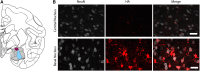
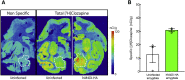
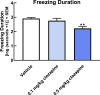
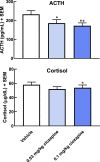
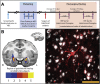
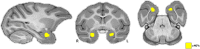
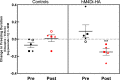
Non-human primate (NHP) models are essential for developing and translating new treatments that target neural circuit dysfunction underlying human psychopathology. As a proof-of-concept for treating neuropsychiatric disorders, we used a NHP model of pathological anxiety to investigate the feasibility of decreasing anxiety by chemogenetically (DREADDs [designer receptors exclusively activated by designer drugs]) reducing amygdala neuronal activity. Intraoperative MRI surgery was used to infect dorsal amygdala neurons with AAV5-hSyn-HA-hM4Di in young rhesus monkeys. In vivo microPET studies with [11C]-deschloroclozapine and postmortem autoradiography with [3H]-clozapine demonstrated selective hM4Di binding in the amygdala, and neuronal expression of hM4Di was confirmed with immunohistochemistry. Additionally, because of its high affinity for DREADDs, and its approved use in humans, we developed an individualized, low-dose clozapine administration strategy to induce DREADD-mediated amygdala inhibition. Compared to controls, clozapine selectively decreased anxiety-related freezing behavior in the human intruder paradigm in hM4Di-expressing monkeys, while coo vocalizations and locomotion were unaffected. These results are an important step in establishing chemogenetic strategies for patients with refractory neuropsychiatric disorders in which amygdala alterations are central to disease pathophysiology.
Keywords: DREADDs; amygdala; anxiety; behavioral inhibition; clozapine; depression; non-human primate; rhesus; stress.
Copyright © 2021 The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests N.H.K. currently receives research support from the National Institute of Mental Health; serves as a consultant to CME Outfitters, the Pritzker Neurospsychiatric Disorders Research Consortium, Skyland Trail Advisory Board, and the Institute of Early Adversity Research External Scientific Advisory Board at the University of Texas – Austin; is a shareholder in Seattle Genetics; has served as co-editor of Psychoneuroendocrinology, and currently serves as Editor-in-Chief of The American Journal of Psychiatry. All other authors report no biomedical financial interests or potential declarations of interest.
Figures


Comment in
-
Clozapine is my favorite color: Chemogenetic modulation of anxiety-related behavior in primates.Mol Ther. 2021 Dec 1;29(12):3322-3324. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.11.001. Epub 2021 Nov 10. Mol Ther. 2021. PMID: 34762818 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
DREADD-mediated amygdala activation is sufficient to induce anxiety-like responses in young nonhuman primates.Curr Res Neurobiol. 2023 Oct 5;5:100111. doi: 10.1016/j.crneur.2023.100111. eCollection 2023. Curr Res Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 38020807 Free PMC article.
-
DREADD-mediated amygdala activation is sufficient to induce anxiety-like responses in young nonhuman primates.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jun 7:2023.06.06.543911. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.06.543911. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Curr Res Neurobiol. 2023 Oct 05;5:100111. doi: 10.1016/j.crneur.2023.100111. PMID: 37333300 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Chemogenetic Inhibition of the Amygdala Modulates Emotional Behavior Expression in Infant Rhesus Monkeys.eNeuro. 2019 Oct 14;6(5):ENEURO.0360-19.2019. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0360-19.2019. Print 2019 Sep/Oct. eNeuro. 2019. PMID: 31541000 Free PMC article.
-
Chemogenetic Tools and their Use in Studies of Neuropsychiatric Disorders.Physiol Res. 2024 Aug 30;73(S1):S449-S470. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.935401. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Physiol Res. 2024. PMID: 38957949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The use of chemogenetic approaches in alcohol use disorder research and treatment.Alcohol. 2019 Feb;74:39-45. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2018.05.012. Epub 2018 Jun 1. Alcohol. 2019. PMID: 30442535 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Update on Nonhuman Primate Models of Brain Disease and Related Research Tools.Biomedicines. 2023 Sep 12;11(9):2516. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11092516. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37760957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What can neuroimaging of neuromodulation reveal about the basis of circuit therapies for psychiatry?Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024 Nov;50(1):184-195. doi: 10.1038/s41386-024-01976-2. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 39198580 Review.
-
Multimodal Imaging for Validation and Optimization of Ion Channel-Based Chemogenetics in Nonhuman Primates.J Neurosci. 2023 Sep 27;43(39):6619-6627. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0625-23.2023. Epub 2023 Aug 24. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37620158 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging-based chemogenetics for dissecting neural circuits in nonhuman primates.Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2024;100(8):476-489. doi: 10.2183/pjab.100.030. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39401901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unsupervised decomposition of natural monkey behavior into a sequence of motion motifs.Commun Biol. 2024 Sep 3;7(1):1080. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06786-2. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39227400 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kessler R.C., Ruscio A.M., Shear K., Wittchen H.U. Epidemiology of anxiety disorders. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2010;2:21–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

