Clinical efficacy of eucaloric ketogenic nutrition in the COVID-19 cytokine storm: A retrospective analysis of mortality and intensive care unit admission
- PMID: 33895559
- PMCID: PMC7937042
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nut.2021.111236
Clinical efficacy of eucaloric ketogenic nutrition in the COVID-19 cytokine storm: A retrospective analysis of mortality and intensive care unit admission
Abstract
Objectives: Our primary objective was to explore the effect of a eucaloric ketogenic diet (EKD) on mortality, admission to the intensive care unit, and need for non-invasive ventilation in hospitalized patients with COronaVIrus Disease 19 (COVID-19), in comparison to a eucaloric standard diet. Secondary objectives were verification of the safety and feasibility of the diet and its effects on inflammatory parameters, particularly interleukin-6.
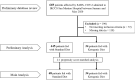
Methods: The study is a retrospective analysis of 34 patients fed with an EKD in comparison to 68 patients fed with a eucaloric standard diet, selected and matched using propensity scores 1:2 to avoid the confounding effect of interfering variables. Our hypothesis was that an EKD would reduce mortality, admission to the intensive care unit, and need for non-invasive ventilation in patients with COVID-19.
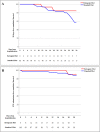
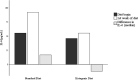
Results: The preliminary multivariate analysis showed a statistically significant difference in survival (P = 0.046) and need for the intensive care unit (P = 0.049) for the EKD compared with a eucaloric standard diet. Even considering the EKD start day as a time-dependent variable, the results maintain a positive trend for application of the diet, and it is not possible to reject the null hypothesis (P < 0.05). Interleukin-6 concentrations between t0 and t7 (7 d after the beginning of the diet) in the ketogenic nutrition group show a trend that is almost significant (P = 0.062). The EKD was safe and no adverse events were observed.
Conclusions: These results show a possible therapeutic role of an EKD in the clinical management of COVID-19. Currently, a prospective controlled randomized trial is running to confirm these preliminary data.
Keywords: Aerobic glycolysis; COVID-19; Cytokine storm syndrome; Hyperglycemia; IL-6; Ketogenic diet; SARS-CoV-2; Warburg effect.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous