Molecular classification improves risk assessment in adult BCR-ABL1-negative B-ALL
- PMID: 33895809
- PMCID: PMC9069478
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2020010144
Molecular classification improves risk assessment in adult BCR-ABL1-negative B-ALL
Abstract
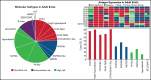
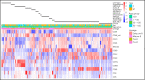
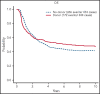
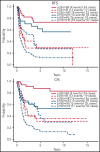
Genomic classification has improved risk assignment of pediatric, but not adult B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL). The international UKALLXII/ECOG-ACRIN E2993 (#NCT00002514) trial accrued 1229 adolescent/adult patients with BCR-ABL1- B-ALL (aged 14 to 65 years). Although 93% of patients achieved remission, 41% relapsed at a median of 13 months (range, 28 days to 12 years). Five-year overall survival (OS) was 42% (95% confidence interval, 39, 44). Transcriptome sequencing, gene expression profiling, cytogenetics, and fusion polymerase chain reaction enabled genomic subtyping of 282 patient samples, of which 264 were eligible for trial, accounting for 64.5% of E2993 patients. Among patients with outcome data, 29.5% with favorable outcomes (5-year OS 65% to 80%) were deemed standard risk (DUX4-rearranged [9.2%], ETV6-RUNX1/-like [2.3%], TCF3-PBX1 [6.9%], PAX5 P80R [4.1%], high-hyperdiploid [6.9%]); 50.2% had high-risk genotypes with 5-year OS of 0% to 27% (Ph-like [21.2%], KMT2A-AFF1 [12%], low-hypodiploid/near-haploid [14.3%], BCL2/MYC-rearranged [2.8%]); 20.3% had intermediate-risk genotypes with 5-year OS of 33% to 45% (PAX5alt [12.4%], ZNF384/-like [5.1%], MEF2D-rearranged [2.8%]). IKZF1 alterations occurred in 86% of Ph-like, and TP53 mutations in patients who were low-hypodiploid (54%) and BCL2/MYC-rearranged (33%) but were not independently associated with outcome. Of patients considered high risk based on presenting age and white blood cell count, 40% harbored subtype-defining genetic alterations associated with standard- or intermediate-risk outcomes. We identified distinct immunophenotypic features for DUX4-rearranged, PAX5 P80R, ZNF384-R/-like, and Ph-like genotypes. These data in a large adult B-ALL cohort treated with a non-risk-adapted approach on a single trial show the prognostic importance of genomic analyses, which may translate into future therapeutic benefits.
© 2021 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures

Comment in
-
ALL is not the same in the era of genetics.Blood. 2021 Sep 16;138(11):915-916. doi: 10.1182/blood.2021011934. Blood. 2021. PMID: 34529020 No abstract available.
References
-
- Rowe JM, Buck G, Burnett AK, et al. ; MRC/NCRI Adult Leukemia Working Party . Induction therapy for adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: results of more than 1500 patients from the international ALL trial: MRC UKALL XII/ECOG E2993. Blood. 2005;106(12):3760-3767. - PubMed
-
- Goldstone AH, Richards SM, Lazarus HM, et al. . In adults with standard-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia, the greatest benefit is achieved from a matched sibling allogeneic transplantation in first complete remission, and an autologous transplantation is less effective than conventional consolidation/maintenance chemotherapy in all patients: final results of the International ALL Trial (MRC UKALL XII/ECOG E2993). Blood. 2008;111(4): 1827-1833. - PubMed
-
- Rowe JM, Buck G, Moorman AV, et al. . Standard consolidation/maintenance chemotherapy is consistently superior to a single autologous transplant for adult patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Results of the international ALL trial (MRC UKALL XII/ECOG E2993) [abstract]. Blood. 2008;112(11). Abstract 3314.
-
- Moorman AV, Harrison CJ, Buck GAN, et al. ; Adult Leukaemia Working Party, Medical Research Council/National Cancer Research Institute . Karyotype is an independent prognostic factor in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL): analysis of cytogenetic data from patients treated on the Medical Research Council (MRC) UKALLXII/Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) 2993 trial. Blood. 2007;109(8):3189-3197. - PubMed
-
- Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL.. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Lyon, France: IARC; 2008
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA198089/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 21019/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- P30 CA118100/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX004662/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R50 CA211542/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA232760/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA021765/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180820/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233332/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM115279/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233290/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 16896/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- UG1 CA233234/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA197695/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 9609/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- UG1 CA189859/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

