Efficacy of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections for Grade 3 Symptomatic Degenerative Meniscal Lesions: A 1-Year Follow-up Prospective Study
- PMID: 33896253
- PMCID: PMC8883415
- DOI: 10.1177/19417381211011074
Efficacy of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections for Grade 3 Symptomatic Degenerative Meniscal Lesions: A 1-Year Follow-up Prospective Study
Abstract
Background: Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections have been proposed as a biologic option to provide symptomatic relief and delay surgery in patients with degenerative joint disease of osteoarthritis (OA). The efficacy of autologous PRP on symptomatic degenerative meniscal lesions (DMLs) has never been investigated.
Hypothesis: We hypothesized that patients with symptomatic DMLs without OA undergoing autologous PRP injections experience a significant clinical improvement at 12 months.
Study design: Prospective case series.
Level of evidence: Level 4.
Methods: A total of 69 patients with symptomatic DMLs without radiographic evidence of knee OA (Kellgren-Lawrence radiographic grading scale 0-1) received 4 autologous PRP injections once a week. Patients were prospectively evaluated before the injection and then at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months. Evaluation was based on Lysholm knee scoring scale (primary outcome), Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Arthritis Index (WOMAC), Tegner activity scale, and visual analogue scale scores.
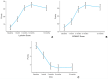
Results: Patients treated with PRP injections demonstrated an improving knee function and symptoms over the duration of the study. A significant improvement from baseline to 12 months was observed in all the outcome measures, and no patients experienced failure or required surgery during the follow-up. Patients younger than 50 years reported lower subjective level of pain and higher Tegner activity scale at baseline and had significantly better Lysholm knee scoring scale (P = 0.03) and WOMAC (P = 0.03) scores at 6 months, as well as better range of motion at 3, 6, and 12 months (P < 0.001). Thirty-three (47.8%) patients were very satisfied, 26 (37.7%) satisfied, 8 (11.6%) partially satisfied, and 2 (2.9 %) not satisfied, with 62 (89.8%) patients willing to repeat the same treatment. No patient was lost to follow-up and no patient experienced adverse reaction, infection, failure, recurrence or underwent further surgery.
Conclusion: PRP injections provide short-term benefits in symptomatic DMLs. Although promising results were evident at 12 months, this is a preliminary study and no definitive recommendation can be made based, for example, on longer follow-up.
Clinical relevance: This research supports the use of autologous PRP injections for symptomatic DMLs.
Keywords: degenerative meniscus; knee; platelet-rich plasma (PRP).
Conflict of interest statement
The following author declared potential conflicts of interest: M.A.-M. prepared the work as employee of University of Genoa.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Hyaluronic Acid Injections for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: Results at 5 Years of a Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Trial.Am J Sports Med. 2019 Feb;47(2):347-354. doi: 10.1177/0363546518814532. Epub 2018 Dec 13. Am J Sports Med. 2019. PMID: 30545242 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of intra-articular injection of combined platelet-rich-plasma (PRP) and hyaluronic acid (HA) in knee degenerative joint disease: a prospective, randomized, double-blind clinical trial.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024 Nov;144(11):5039-5051. doi: 10.1007/s00402-024-05603-z. Epub 2024 Oct 5. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024. PMID: 39367905 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical outcome and risk factor predictive for failure of autologous PRP injections for low-to-moderate knee osteoarthritis.J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2021 May-Aug;29(2):23094990211021922. doi: 10.1177/23094990211021922. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2021. PMID: 34180298
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Hyaluronic Acid for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Am J Sports Med. 2021 Jan;49(1):249-260. doi: 10.1177/0363546520909397. Epub 2020 Apr 17. Am J Sports Med. 2021. PMID: 32302218
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma Combined With Hyaluronic Acid Improves Pain and Function Compared With Hyaluronic Acid Alone in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Arthroscopy. 2021 Apr;37(4):1277-1287.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2020.11.052. Epub 2020 Dec 3. Arthroscopy. 2021. PMID: 33278533
Cited by
-
Platelet-rich plasma for nonoperative management of degenerative meniscal tears: A systematic review.J Orthop. 2024 Mar 12;54:67-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jor.2024.03.009. eCollection 2024 Aug. J Orthop. 2024. PMID: 39036807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma Gel Matrix (PRP-GM): Description of a New Technique.Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Dec 19;9(12):817. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9120817. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551023 Free PMC article.
-
Degenerative Meniscus Tears Treated Nonoperatively With Platelet-Rich Plasma Yield Variable Clinical and Imaging Outcomes: A Systematic Review.Arthrosc Sports Med Rehabil. 2024 Feb 23;6(2):100916. doi: 10.1016/j.asmr.2024.100916. eCollection 2024 Apr. Arthrosc Sports Med Rehabil. 2024. PMID: 38525288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) augmentation does not result in more favourable outcomes in arthroscopic meniscal repair: a meta-analysis.J Orthop Traumatol. 2022 Feb 7;23(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s10195-022-00630-1. J Orthop Traumatol. 2022. PMID: 35129728 Free PMC article.
-
No Long-Term Superiority of Cord-Derived PRP over Autologous PRP in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Prospective Cohort Study.J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. 2025 Apr 21;10(2):138. doi: 10.3390/jfmk10020138. J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. 2025. PMID: 40566434 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alessio-Mazzola M, Repetto I, Biti B, Trentini R, Formica M, Felli L. Autologous US-guided PRP injection versus US-guided focal extracorporeal shock wave therapy for chronic lateral epicondylitis: a minimum of 2-year follow-up retrospective comparative study. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2018;26:2309499017749986. - PubMed
-
- Andia I, Maffulli N. A contemporary view of platelet-rich plasma therapies: moving toward refined clinical protocols and precise indications. Regen Med. 2018;13:717-728. - PubMed
-
- Andia I, Maffulli N. Biological therapies in regenerative sports medicine. Sports Med. 2017;47:807-828. - PubMed
-
- Bellamy N, Wells G, Campbell J. Relationship between severity and clinical importance of symptoms in osteoarthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 1991;10:138-143. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

