Evaluation of the antioxidant capacity of bioactive compounds and determination of proline in honeys from Pará
- PMID: 33897026
- PMCID: PMC8021653
- DOI: 10.1007/s13197-020-04701-1
Evaluation of the antioxidant capacity of bioactive compounds and determination of proline in honeys from Pará
Abstract
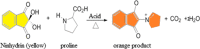
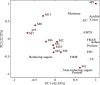
Honey is a viscous food, being a complex mixture of substances, among them the main components of honey are: water, minerals, sugars, organic acids, and proteins (enzymes and amino acids). Honey has in its composition compounds that can provide antioxidant properties such as phenolic compounds. This work aimed to evaluate the nutritional composition, the antioxidant capacity of bioactive compounds and to quantify proline in honeys from Pará. Chemical (moisture, protein and ash), physicochemical (hydroxymethylfurfural, reducing and non-reducing sugars, acidity, pH and electrical conductivity) and physical (color) analysis were conducted. Phenolic compounds, flavonoids, antioxidant capacity (ABTS*+ and FRAP), and proline were also evaluated. 62.5% of Apis bee honeys were not within the moisture standards, for stingless bees, there is no official legislation. All the honeys analyzed were within the limit of the legislation in relation to the amount of HMF. High amounts of protein were found, in relation to the consulted literature. The phenolic compounds varied from 4.27 to 145.43 mg/100 g, the flavonoids varied from 2.75 to 18.76 mg/100 g, with higher values than in the literature consulted. The antioxidant capacity by ABTS*+ and FRAP methods had excellent values, being superior to the various works with honey from Brazil and the world. The proline ranged from 6.25 to 144.70 mg/kg. With these results, it was proven that amazonian honeys have antioxidant activity, but the honey harvest needs to be improved, so as not to harm the nutritional components found in its composition.
Keywords: Antioxidant; Correlation; Honey; Proline.
© Association of Food Scientists & Technologists (India) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestNo potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Almeida-muradian LB, Sousa RJ, Barth OM, Gallmann P. Preliminary data on Brazilian monofloral honey from the northeast region using FT-IR ATR spectroscopic, palynological and color analysis. Quim Nova. 2014;37:716–719. doi: 10.5935/0100-4042.20140115. - DOI
-
- AOAC (2005) Association of Official Analytical Chemistry. In: Horwitz W (ed), 18th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemistry, Gaithersburg
-
- Azeredo LC, Azeredo SRS, Dutra VML. Protein contents and physicochemical properties in honey samples of Apis mellifera of different floral origins. Food Chem. 2003;80:249–254. doi: 10.1016/S0308-8146(02)00261-3. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
