MicroRNA Expression Differences in Blood-Derived CD19+ B Cells of Methotrexate Treated Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
- PMID: 33897713
- PMCID: PMC8062711
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.663736
MicroRNA Expression Differences in Blood-Derived CD19+ B Cells of Methotrexate Treated Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
Abstract
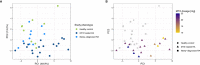
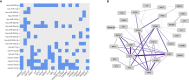
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a complex disease with a wide range of underlying susceptibility factors. Recently, dysregulation of microRNAs (miRNAs) in RA have been reported in several immune cell types from blood. However, B cells have not been studied in detail yet. Given the autoimmune nature of RA with the presence of autoantibodies, CD19+ B cells are a key cell type in RA pathogenesis and alterations in CD19+ B cell subpopulations have been observed in patient blood. Therefore, we aimed to reveal the global miRNA repertoire and to analyze miRNA expression profile differences in homogenous RA patient phenotypes in blood-derived CD19+ B cells. Small RNA sequencing was performed on CD19+ B cells of newly diagnosed untreated RA patients (n=10), successfully methotrexate (MTX) treated RA patients in remission (MTX treated RA patients, n=18) and healthy controls (n=9). The majority of miRNAs was detected across all phenotypes. However, significant expression differences between MTX treated RA patients and controls were observed for 27 miRNAs, while no significant differences were seen between the newly diagnosed patients and controls. Several of the differentially expressed miRNAs were previously found to be dysregulated in RA including miR-223-3p, miR-486-3p and miR-23a-3p. MiRNA target enrichment analysis, using the differentially expressed miRNAs and miRNA-target interactions from miRTarBase as input, revealed enriched target genes known to play important roles in B cell activation, differentiation and B cell receptor signaling, such as STAT3, PRDM1 and PTEN. Interestingly, many of those genes showed a high degree of correlated expression in CD19+ B cells in contrast to other immune cell types. Our results suggest important regulatory functions of miRNAs in blood-derived CD19+ B cells of MTX treated RA patients and motivate for future studies investigating the interactive mechanisms between miRNA and gene targets, as well as the possible predictive power of miRNAs for RA treatment response.
Keywords: CD19+ B cells; NGS; methotrexate; miRNA; microRNA; rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2021 Heinicke, Zhong, Flåm, Breidenbach, Leithaug, Mæhlen, Lillegraven, Aga, Norli, Mjaavatten, Haavardsholm, Zucknick, Rayner and Lie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Smolen JS, Landewé RBM, Bijlsma JWJ, Burmester GR, Dougados M, Kerschbaumer A, et al. . EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2019 update. Ann Rheumatic Dis (2020) 79(6):685–99. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216655 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Emery P, Breedveld FC, Hall S, Durez P, Chang DJ, Robertson D, et al. . Comparison of methotrexate monotherapy with a combination of methotrexate and etanercept in active, early, moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (COMET): a randomised, double-blind, parallel treatment trial. Lancet (2008) 372(9636):375–82. 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61000-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bijlsma JWJ, Welsing PMJ, Woodworth TG, Middelink LM, Pethö-Schramm A, Bernasconi C, et al. . Early rheumatoid arthritis treated with tocilizumab, methotrexate, or their combination (U-Act-Early): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, double-dummy, strategy trial. Lancet (2016) 388(10042):343–55. 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30363-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Verstappen SM, Jacobs JW, van der Veen MJ, Heurkens AH, Schenk Y, ter Borg EJ, et al. . Intensive treatment with methotrexate in early rheumatoid arthritis: aiming for remission. Computer Assisted Management in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis (CAMERA, an open-label strategy trial). Ann Rheumatic Dis (2007) 66(11):1443–9. 10.1136/ard.2007.071092 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nielen MM, van Schaardenburg D, Reesink HW, van de Stadt RJ, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE, de Koning MH, et al. . Specific autoantibodies precede the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis: a study of serial measurements in blood donors. Arthritis Rheumatol (2004) 50(2):380–6. 10.1002/art.20018 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

