Stereotactic body radiotherapy for the treatment of oligometastatic gynecological malignancy in the abdomen and pelvis: A single-institution experience
- PMID: 33898082
- PMCID: PMC8055243
Stereotactic body radiotherapy for the treatment of oligometastatic gynecological malignancy in the abdomen and pelvis: A single-institution experience
Abstract
Purpose/objectives: Metastasis-directed therapy with stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) in the setting of oligometastatic disease is a rapidly evolving paradigm given ongoing improvements in systemic therapies and diagnostic modalities. However, SBRT to targets in the abdomen and pelvis is historically associated with concerns about toxicity. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of SBRT to the abdomen and pelvis for women with oligometastases from primary gynecological tumors.
Materials/methods: From our IRB-approved registry, all patients who were treated with SBRT between 2014 and 2020 were identified. Oligometastatic disease was defined as 1 to 5 discrete foci of clinical metastasis radiographically diagnosed by positron emission tomography (PET) and/or computerized tomography (CT) imaging. The primary endpoint was local control at 12 months. Local and distant control rates were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method. Time intervals for development of local progression and distant progression were calculated based on follow up visits with re-staging imaging. Acute and late toxicity outcomes were determined based on Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 5.0.
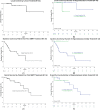
Results: We identified 34 women with 43 treated lesions. Median age was 68 years (range 32-82), and median follow up time was 12 months (range 0.2-54.0). Most common primary tumor sites were ovarian (n=12), uterine (n=11), and cervical (n=7). Median number of previous lines of systemic therapy agents at time of SBRT was 2 (range 0-10). Overall, SBRT was delivered to 1 focus of oligometastasis in 29 cases, 2 foci in 2 cases, 3 foci in 2 cases, and 4 foci in 1 case. All patients were treated comprehensively with SBRT to all sites of oligometastasis. Median prescription dose was 24 Gy (range 18-54 Gy) in 3 fractions (range 3-6) to a median prescription isodose line of 83.5% (range 52-95). Local control by lesion at 12 and 24 months was 92.5% for both time points. Local failure was observed in three treated sites among two patients, two of which were at 11 months in one patient, and the other at 30 months. Systemic control rate was 60.2% at 12 months. Overall survival at 12 and 24 months was 85% and 70.2%, respectively. Acute grade 2 toxicities included nausea (n=3), and there were no grade > 3 acute toxicities. Late grade 1 toxicities included diarrhea (n=1) and fatigue (n=1), and there were no grade > 2 toxicities.
Conclusion: SBRT to oligometastatic gynecologic malignancies in the abdomen and pelvis is feasible with encouraging preliminary safety and local control outcomes. This approach is associated with excellent local control and low rates of toxicity during our follow-up interval. Further investigations into technique, dose-escalation and utilization are warranted.
Keywords: Oligometastasis; gynecological malignancies; radiotherapy; stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT).
© 2021 Old City Publishing, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ disclosure of potential conflicts of interest The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Hellman S, Weichselbaum RR. Oligometastases. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 1995;13(1):8-10. - PubMed
-
- Milano MT, Biswas T, Simone CB. (2nd), Lo SS. Oligometastases: history of a hypothesis. Annals of palliative medicine. 2020. - PubMed
-
- Guckenberger M, Lievens Y, Bouma AB, Collette L, Dekker A, deSouza NM, Dingemans AC, Fournier B, Hurkmans C, Lecouvet FE, Meattini I, Méndez Romero A, Ricardi U, Russell NS, Schanne DH, Scorsetti M, Tombal B, Verellen D, Verfaillie C, Ost P. Characterisation and classification of oligometastatic disease: a European Society for Radiotherapy and Oncology and European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer consensus recommendation. The Lancet Oncology. 2020;21(1):e18-e28. - PubMed
-
- Lievens Y, Guckenberger M, Gomez D, Hoyer M, Iyengar P, Kindts I, Méndez Romero A, Nevens D, Palma D, Park C, Ricardi U, Scorsetti M, Yu J, Woodward WA. Defining oligometastatic disease from a radiation oncology perspective: An ESTRO-ASTRO consensus document. Radiotherapy and oncology : journal of the European Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology. 2020;148:157-166. - PubMed
-
- Palma DA, Olson R, Harrow S, Correa RJM, Schneiders F, Haasbeek CJA, Rodrigues GB, Lock M, Yaremko BP, Bauman GS, Ahmad B, Schellenberg D, Liu M, Gaede S, Laba J, Mulroy L, Senthi S, Louie AV, Swaminath A, Chalmers A, Warner A, Slotman BJ, de Gruijl TD, Allan A, Senan S. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for the comprehensive treatment of 4-10 oligometastatic tumors (SABR-COMET-10): study protocol for a randomized phase III trial. BMC cancer. 2019;19(1):816. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
