Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Corticosteroid Injection for Lumbar Spondylosis and Sacroiliac Arthropathy: A Systematic Review of Comparative Studies
- PMID: 33898145
- PMCID: PMC8061754
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.14062
Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Corticosteroid Injection for Lumbar Spondylosis and Sacroiliac Arthropathy: A Systematic Review of Comparative Studies
Abstract
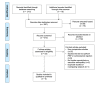
This systematic review compares clinical outcomes between platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and corticosteroid injections for the treatment of lumbar spondylosis and sacroiliac arthropathy. A systematic review was registered with the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) and performed according to Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines using the Pubmed, SCOPUS, and Ovid MEDLINE databases. All level I-III evidence comparative studies published in the English language investigating the clinical outcomes between PRP and corticosteroid injections for the treatment of lumbar spondylosis and sacroiliac arthropathy were included. Five studies (242 patients, 114 PRP, 128 corticosteroid) were analyzed. One randomized study was level I evidence, two randomized studies were level II, and two non-randomized studies were level III. Final follow-up ranged from six weeks to six months. Four studies found that both PRP and corticosteroid treatment led to a statistically significant reduction in the visual analog scale (VAS). One found that only the PRP group led to a statistically significant reduction in VAS. Three studies found more significant improvements in one or more clinical outcome scores among PRP patients as compared with corticosteroid patients at the three- to six-month follow-up. Two studies found no difference in outcome score improvements between the two groups at six- to 12-week follow-up. There were no reports of major complications. There were no significant differences in minor complication rates between the two groups. In conclusion, both PRP and corticosteroid injections are safe and effective options for the treatment of lumbar spondylosis and sacroiliac arthropathy. There is some evidence that PRP injection is a more effective option at long-term follow-up compared with corticosteroid injection. Further randomized controlled trials with longer-term follow-up are necessary to compare its long-term efficacy.
Keywords: corticosteroid; injection; lumbar spondylosis; pain management; platelet-rich plasma; sacroiliac arthropathy.
Copyright © 2021, Ling et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Takashi Hirase was supported by a Burroughs Wellcome Fund Physician-Scientist Institutional Award to the Texas A&M University Academy of Physician Scientists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection Can Be a Viable Alternative to Corticosteroid Injection for Conservative Treatment of Rotator Cuff Disease: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Arthroscopy. 2023 Feb;39(2):402-421.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2022.06.022. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Arthroscopy. 2023. PMID: 35810976 Review.
-
Autologous growth factor injections in chronic tendinopathy.J Athl Train. 2014 May-Jun;49(3):428-30. doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-49.3.06. Epub 2014 May 19. J Athl Train. 2014. PMID: 24840581 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of corticosteroid versus platelet-rich plasma injection therapies for the management of lateral epicondylitis: A systematic review.SICOT J. 2018;4:11. doi: 10.1051/sicotj/2017062. Epub 2018 Mar 21. SICOT J. 2018. PMID: 29561260 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of a Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection and a Conventional Steroid Injection for Pain Relief and Functional Improvement of Partial Supraspinatus Tears.Orthop J Sports Med. 2021 Sep 1;9(9):23259671211024937. doi: 10.1177/23259671211024937. eCollection 2021 Sep. Orthop J Sports Med. 2021. PMID: 34485587 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation Methods and Clinical Outcomes of Platelet-Rich Plasma for Intra-articular Hip Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials.Orthop J Sports Med. 2020 Oct 29;8(10):2325967120960414. doi: 10.1177/2325967120960414. eCollection 2020 Oct. Orthop J Sports Med. 2020. PMID: 33195721 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of platelet-rich plasma versus steroid injection in plantar fasciitis: a randomized clinical trial.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023 Mar 7;24(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s12891-023-06277-1. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023. PMID: 36882804 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines on Regenerative Medicine Treatment for Chronic Pain: A Consensus Report from a Multispecialty Working Group.J Pain Res. 2024 Sep 11;17:2951-3001. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S480559. eCollection 2024. J Pain Res. 2024. PMID: 39282657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of intra-articular injection of autologous platelet-rich plasma versus corticosteroids in the treatment of synovitis in lumbar facet joint disease.Saudi Med J. 2022 Nov;43(11):1200-1208. doi: 10.15537/smj.2022.43.11.20220449. Saudi Med J. 2022. PMID: 36379530 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Autologous Platelet Rich Fibrin Versus Steroid in Ultrasound-Guided Sacroiliac Joint Injection for Joint Dysfunction: Randomized Comparative Study.Anesth Pain Med. 2025 Feb 16;15(1):e158219. doi: 10.5812/aapm-158219. eCollection 2025 Feb 28. Anesth Pain Med. 2025. PMID: 40421261 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet-rich plasma versus corticosteroid injections in the management of patients with rotator cuff disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Orthop Res. 2023 Jan;41(1):7-20. doi: 10.1002/jor.25463. Epub 2022 Oct 31. J Orthop Res. 2023. PMID: 36250611 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials