Korean traditional herbal formula Soshiho-tang attenuates memory impairment and neuronal damage in mice with amyloid-beta-induced Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 33898246
- PMCID: PMC8059063
- DOI: 10.1016/j.imr.2021.100723
Korean traditional herbal formula Soshiho-tang attenuates memory impairment and neuronal damage in mice with amyloid-beta-induced Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
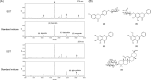
Background: Soshiho-tang (SST), also known as Xiaochaihu-tang in China and Sho-saiko-to in Japan, is an Oriental herbal formula traditionally used to treat febrile diseases. Recently, several in vitro and in vivo studies have reported the anti-cancer, anti-liver disease, and anti-inflammatory activities of SST. However, there is little evidence of its effects on neurological diseases. We previously reported the inhibitory effects of SST on in vitro acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activation and amyloid-β (Aβ) aggregation, which are crucial hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease (AD). In the present study, we report that SST has preventive effects on memory impairment and neuronal cell changes in an Aβ-induced AD-like mouse model.
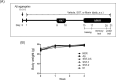
Methods: Male mice underwent injection of Aβ aggregates and administered SST (500, 1,000, or 2,000 mg/kg/day) for 20 days. Behavioral tests (passive avoidance task [PAT] and Morris water maze [MWM] test) were conducted. Lastly, brain sections were obtained from sacrificed mice for quantitative analysis.
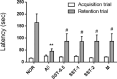
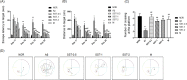
Results: Intracerebroventricular (ICV) injection of Aβ aggregates significantly decreased the latency time in the PAT and MWM test compared to normal control. In contrast, SST administration markedly reversed the latency caused by Aβ injection. Additionally, our data revealed that SST-mediated improvements in memory impairment are related to its neuroprotective and anti-neuroinflammatory effects. On histological analysis, SST treatment protected neuronal loss and damage as well as microglial activation, and ameliorated amount of Aβ in brain of mouse model of AD.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that SST may be a promising candidate for the development of novel drugs for AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Anti-neuroinflammation; Memory improvement; Neuroprotection; Soshiho-tang.
© 2021 Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine.
Figures
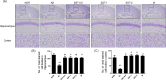
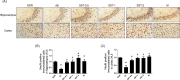
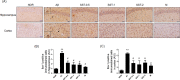
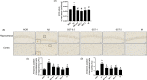
Similar articles
-
Bojungikgi-Tang, a Traditional Herbal Formula, Exerts Neuroprotective Effects and Ameliorates Memory Impairments in Alzheimer's Disease-Like Experimental Models.Nutrients. 2018 Dec 10;10(12):1952. doi: 10.3390/nu10121952. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30544702 Free PMC article.
-
6-Methyluracil derivatives as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors for treatment of Alzheimer's disease.Int J Risk Saf Med. 2015;27 Suppl 1:S69-71. doi: 10.3233/JRS-150694. Int J Risk Saf Med. 2015. PMID: 26639718
-
Formulated Chinese medicine Shaoyao Gancao Tang reduces NLRP1 and NLRP3 in Alzheimer's disease cell and mouse models for neuroprotection and cognitive improvement.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Jun 9;13(11):15620-15637. doi: 10.18632/aging.203125. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34106880 Free PMC article.
-
Samhwangsasim-tang attenuates neuronal apoptosis and cognitive decline through BDNF-mediated activation of tyrosin kinase B and p75-neurotrophin receptors.Phytomedicine. 2022 May;99:153997. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.153997. Epub 2022 Feb 25. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35279612
-
Ficus erecta Thunb. Leaves Ameliorate Cognitive Deficit and Neuronal Damage in a Mouse Model of Amyloid-β-Induced Alzheimer's Disease.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 15;12:607403. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.607403. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33935701 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Potential Role of Phytochemicals in Alzheimer's Disease.Nutrients. 2025 Feb 12;17(4):653. doi: 10.3390/nu17040653. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40004981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic effects of total saikosaponins from Radix bupleuri against Alzheimer's disease.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 21;13:940999. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.940999. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35935875 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the therapeutic potential of natural products in Alzheimer's disease: insights from in vitro, in vivo, and clinical studies.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 23;16:1601712. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1601712. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40626308 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baik YS. A study on the complex efficacy of Sosihotang. J Kor Med Class. 2014;27(2):137.
-
- Kim A, Im M, Ma JY. Sosiho‑tang ameliorates cachexia-related symptoms in mice bearing colon 26 adenocarcinoma by reducing systemic inflammation and muscle loss. Oncol Rep. 2016;35(3):1841–1850. - PubMed
-
- Mizushima Y, Kashii T, Tokimitsu Y. Cytotoxic effect of herbal medicine sho-saiko-to on human lung-cancer cell-lines in-vitro. Oncol Rep. 1995;2(1):91–94. - PubMed
-
- Lee JK, Kim JH, Shin HK. Therapeutic effects of the oriental herbal medicine Sho-saiko-to on liver cirrhosis and carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 2011;41(9):825–837. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

