Electroacupuncture anesthesia for laparotomy in goats
- PMID: 33898284
- PMCID: PMC8057214
- DOI: 10.4314/ovj.v11i1.9
Electroacupuncture anesthesia for laparotomy in goats
Abstract
Background: The objective of the study to evaluate the effect of electroacupuncture during laparotomy in goats.
Aim: To study the abdominal anesthesia in goats by electroacupuncture using the physiological variables, vital parameters, hematological, biochemical, cortisol hormone, pain threshold, and wound healing for laparotomy in goats.
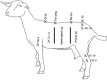
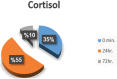
Methods: Fifteen healthy adult bucks were used to receive electroacupuncture in 10 newly selected acupoints. The data (M ± SD) were assessed at intervals (0 minutes) before induction (control group), (5 minutes), (10 minutes), (15 minutes), and (20 minutes) during induction, (30 minutes), (45 minutes), and (60 minutes) throughout surgery and (24 hours) after surgery, cortisol levels in serum at (0), (24 hours), and (72 hours) throughout laparotomy.
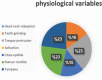
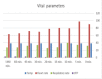
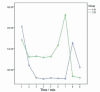
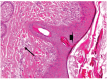
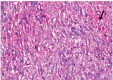
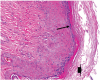
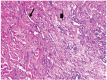
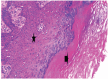
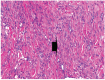
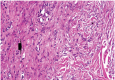
Results: The goats of the study showed improvement in the rates of eyelid closure, head, and neck relaxation, rumen motility, and tympany which were graded into mild (+), moderate (++), and severe (+++) degrees. The respiratory rates, body temperatures, and capillary fill times were not significantly different. The total mean of hematocrit was (19.9 ± 2.68), the total mean of hemoglobin was (9.9 ± 0.94), the total mean of red blood cells was (7.9 ± 0.8), the total mean of platelets was (244,861.3 ± 138,444.8) and the total mean of SPO2 was (70.5 ± 4.6). ALT and AST showed no significance. The significant mean cortisol level was (2.6 ± 2.01) and the significant mean pain threshold level was (0.02 ± 0.03). The results proved that electroacupuncture had a lot of significant parameters. The wound healing was improved by early epithelization and immature granulation tissue (at 7 days). Thick keratinized epithelization and collagen deposition in the dermal tissue with enhanced angiogenesis (at 14 days). Mild restoration of skin and the dermal tissue was well-organized (at 21 days). Besides, well-formed scar tissue covering a highly cellular organized dermal tissue (at 28 days).
Conclusions: Electroacupuncture had been considered a powerful anesthetic for abdominal surgery in goats. Moreover, wound healing proved excellent and better healing.
Keywords: Acupuncture; Anesthesia; Electroacupuncture; Goat; Laparotomy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Aiello S.E, Moses M.A, Allen D.G. The Merck veterinary manual Merck. 2016:3174–3185.
-
- Asayama K, Ohkubo T, Metoki H, Obara T, Inoue R, Kikuya M, Thijs L, Staessen J.A, Imai Y. Hypertension Objective Treatment Based on Measurement by Electrical Devices of Blood Pressure (HOMED-BP). Cardiovascular outcomes in the first trial of antihypertensive therapy guided by self-measured home blood pressure. Hypertens. Res. 2012;35(11):1102–1110. - PubMed
-
- Bancroft D, Stevens A, Turner R. 4th. Edinburgh, London, Melbourne: Churchill Livingstone; 2012. Theory and practice of histological technique.
-
- Burk K.M, Orr J.A. A procedure for determining subject-specific pulse oxygen saturation response. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2020;58(4):753–761. - PubMed
-
- Cadoy J.M, Acorda J.A. Physiological responses, cortisol level and analgesia in goats subjected to exploratory laparotomy under acupuncture and regional analgesia. J. Vet. Med. 2018;55(1):35–44.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
