Mitochondria Donation by Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Current Understanding and Mitochondria Transplantation Strategies
- PMID: 33898449
- PMCID: PMC8058353
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.653322
Mitochondria Donation by Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Current Understanding and Mitochondria Transplantation Strategies
Abstract
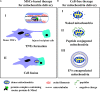
The phenomenon of mitochondria donation is found in various tissues of humans and animals and is attracting increasing attention. To date, numerous studies have described the transfer of mitochondria from stem cells to injured cells, leading to increased ATP production, restoration of mitochondria function, and rescue of recipient cells from apoptosis. Mitochondria transplantation is considered as a novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of mitochondrial diseases and mitochondrial function deficiency. Mitochondrial dysfunction affects cells with high energy needs such as neural, skeletal muscle, heart, and liver cells and plays a crucial role in type 2 diabetes, as well as Parkinson's, Alzheimer's diseases, ischemia, stroke, cancer, and age-related disorders. In this review, we summarize recent findings in the field of mitochondria donation and mechanism of mitochondria transfer between cells. We review the existing clinical trials and discuss advantages and disadvantages of mitochondrial transplantation strategies based on the injection of stem cells, isolated functional mitochondria, or EVs containing mitochondria.
Keywords: cell fusion; extracellular vesicles; isolated mitochondria; mitochondria donation; mitochondria transplantation; tunneling nanotubes.
Copyright © 2021 Gomzikova, James and Rizvanov.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Babenko V. A., Silachev D. N., Zorova L. D., Pevzner I. B., Khutornenko A. A., Plotnikov E. Y., et al. (2015). Improving the post-stroke therapeutic potency of mesenchymal multipotent stromal cells by cocultivation with cortical neurons: the role of crosstalk between cells. Stem Cell Transl Med. 4 1011–1020. 10.5966/sctm.2015-0010 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

