Neutrophil Extracellular Traps: A Perspective of Neuroinflammation and Complement Activation in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 33898514
- PMCID: PMC8060499
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.630869
Neutrophil Extracellular Traps: A Perspective of Neuroinflammation and Complement Activation in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
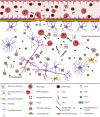
Complement system (CS) components are associated with Alzheimer's disease (AD), the commonest cause of dementia in the world. Neutrophils can be attracted to amyloid-β plaques by several pro-inflammatory factors, including the complement anaphylatoxin C5a. They may release neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), which are chromatin nets associated with myeloperoxidase, elastase, and other enzymes. Some CS molecules, such as C5a, C1q, and CR1, are associated with increased neutrophil recruitment and NETs release. However, the relationship between CS molecules and NETs in AD is poorly understood. In this work, we detected higher NET concentrations in plasma and serum of Brazilian AD patients, than in elderly controls (medians = 2.78 [2.07-6.19] vs. 2.23 [0.33-4.14] ng/mL, p = 0.0005). We discussed these results within the context of our former findings on complement and AD and the context of the literature on complement and NET release, suggesting both as possible therapeutic targets to prevent the progress of the disease.
Keywords: Alzheimer's Disease; C1q; C5a; CR1; complement system; inflammation; neutrophil extracellular traps.
Copyright © 2021 Kretzschmar, Bumiller-Bini, Gasparetto Filho, Zonta, Yu, de Souza, Dias-Melicio and Boldt.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
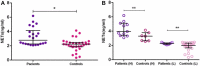
Similar articles
-
Neutrophil extracellular traps can activate alternative complement pathways.Clin Exp Immunol. 2015 Sep;181(3):518-27. doi: 10.1111/cei.12654. Epub 2015 Jun 22. Clin Exp Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25963026 Free PMC article.
-
NETosing Neutrophils Activate Complement Both on Their Own NETs and Bacteria via Alternative and Non-alternative Pathways.Front Immunol. 2016 Apr 14;7:137. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00137. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27148258 Free PMC article.
-
Active immunization against complement factor C5a: a new therapeutic approach for Alzheimer's disease.J Neuroinflammation. 2015 Aug 16;12:150. doi: 10.1186/s12974-015-0369-6. J Neuroinflammation. 2015. PMID: 26275910 Free PMC article.
-
NETosis in Alzheimer's Disease.Front Immunol. 2017 Mar 2;8:211. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00211. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28303140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial Dysfunction Induced by Extracellular Neutrophil Traps Plays Important Role in the Occurrence and Treatment of Extracellular Neutrophil Traps-Related Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 17;23(10):5626. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105626. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628437 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biomimetic engineering of a neuroinflammation-targeted MOF nanozyme scaffolded with photo-trigger released CO for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.Chem Sci. 2024 Jul 18;15(33):13201-13208. doi: 10.1039/d4sc02598a. eCollection 2024 Aug 22. Chem Sci. 2024. PMID: 39183930 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the Extracellular Traps in Central Nervous System.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 16;12:783882. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.783882. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34868063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Intermittent Hypoxia-Hyperoxia on Performance- and Health-Related Outcomes in Humans: A Systematic Review.Sports Med Open. 2022 May 31;8(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s40798-022-00450-x. Sports Med Open. 2022. PMID: 35639211 Free PMC article.
-
The neutrophil extracellular traps in neurological diseases: an update.Clin Exp Immunol. 2024 Nov 12;218(3):264-274. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxae057. Clin Exp Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38975702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene Regulation of Neutrophils Mediated Liver and Lung Injury through NETosis in Acute Pancreatitis.Inflammation. 2025 Feb;48(1):393-411. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02071-w. Epub 2024 Jun 17. Inflammation. 2025. PMID: 38884700
References
-
- Abrams S. T., Morton B., Alhamdi Y., Alsabani M., Lane S., Welters I. D., et al. (2019). A novel assay for neutrophil extracellular trap formation independently predicts disseminated intravascular coagulation and mortality in critically ill patients. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 200, 869–880. 10.1164/rccm.201811-2111OC - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alzheimer’s-Association(2020). Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 16, 391–460. 10.1002/alz.12068 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

