Deep Mutational Scanning of Viral Glycoproteins and Their Host Receptors
- PMID: 33898517
- PMCID: PMC8062978
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.636660
Deep Mutational Scanning of Viral Glycoproteins and Their Host Receptors
Abstract
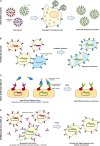
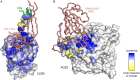
Deep mutational scanning or deep mutagenesis is a powerful tool for understanding the sequence diversity available to viruses for adaptation in a laboratory setting. It generally involves tracking an in vitro selection of protein sequence variants with deep sequencing to map mutational effects based on changes in sequence abundance. Coupled with any of a number of selection strategies, deep mutagenesis can explore the mutational diversity available to viral glycoproteins, which mediate critical roles in cell entry and are exposed to the humoral arm of the host immune response. Mutational landscapes of viral glycoproteins for host cell attachment and membrane fusion reveal extensive epistasis and potential escape mutations to neutralizing antibodies or other therapeutics, as well as aiding in the design of optimized immunogens for eliciting broadly protective immunity. While less explored, deep mutational scans of host receptors further assist in understanding virus-host protein interactions. Critical residues on the host receptors for engaging with viral spikes are readily identified and may help with structural modeling. Furthermore, mutations may be found for engineering soluble decoy receptors as neutralizing agents that specifically bind viral targets with tight affinity and limited potential for viral escape. By untangling the complexities of how sequence contributes to viral glycoprotein and host receptor interactions, deep mutational scanning is impacting ideas and strategies at multiple levels for combatting circulating and emergent virus strains.
Keywords: deep mutational scan; entry receptor; mutational landscape; selection; viral escape; viral fusion protein; virus spike.
Copyright © 2021 Narayanan and Procko.
Conflict of interest statement
EP was the inventor on patent filings by the University of Illinois covering soluble decoy receptors. EP was a co-founder of Orthogonal Biologics, Inc. The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Conformational Engineering of HIV-1 Env Based on Mutational Tolerance in the CD4 and PG16 Bound States.J Virol. 2019 May 15;93(11):e00219-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00219-19. Print 2019 Jun 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30894475 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Mutational Scanning Comprehensively Maps How Zika Envelope Protein Mutations Affect Viral Growth and Antibody Escape.J Virol. 2019 Nov 13;93(23):e01291-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01291-19. Print 2019 Dec 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31511387 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary Landscapes of Host-Virus Arms Races.Annu Rev Immunol. 2022 Apr 26;40:271-294. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-072621-084422. Epub 2022 Jan 26. Annu Rev Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35080919 Review.
-
Diversity of Functionally Permissive Sequences in the Receptor-Binding Site of Influenza Hemagglutinin.Cell Host Microbe. 2017 Jun 14;21(6):742-753.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2017.05.011. Cell Host Microbe. 2017. PMID: 28618270 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Molecule FRET Imaging of Virus Spike-Host Interactions.Viruses. 2021 Feb 21;13(2):332. doi: 10.3390/v13020332. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33669922 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deep mutational scans of XBB.1.5 and BQ.1.1 reveal ongoing epistatic drift during SARS-CoV-2 evolution.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Sep 12:2023.09.11.557279. doi: 10.1101/2023.09.11.557279. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: PLoS Pathog. 2023 Dec 29;19(12):e1011901. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011901. PMID: 37745441 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Deep mutational scanning reveals sequence to function constraints for SWEET family transporters.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 2:2024.06.28.601307. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.28.601307. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39005363 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Deep mutational scanning: A versatile tool in systematically mapping genotypes to phenotypes.Front Genet. 2023 Jan 12;14:1087267. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1087267. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36713072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Machine Learning Variant Effect Prediction Tools for Protein Engineering.Ind Eng Chem Res. 2022 May 18;61(19):6235-6245. doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.1c04943. Epub 2022 Apr 6. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2022. PMID: 36051311 Free PMC article.
-
Deep mutational scans of XBB.1.5 and BQ.1.1 reveal ongoing epistatic drift during SARS-CoV-2 evolution.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Dec 29;19(12):e1011901. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011901. eCollection 2023 Dec. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 38157379 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

