Clinical Utility of Fluid Volume Assessment in Heart Failure Patients Using Bioimpedance Spectroscopy
- PMID: 33898536
- PMCID: PMC8060148
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.636718
Clinical Utility of Fluid Volume Assessment in Heart Failure Patients Using Bioimpedance Spectroscopy
Abstract
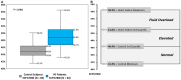
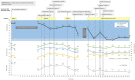
Background: Bioimpedance spectroscopy (BIS) is a non-invasive method used to measure fluid volumes. In this report, we compare BIS measurements from patients with heart failure (HF) to those from healthy adults, and describe how these point-of-care fluid volume assessments may be applied to HF management. Methods and results: Fluid volumes were measured in 64 patients with NYHA class II or III HF and 69 healthy control subjects. BIS parameters including extracellular fluid (ECF), intracellular fluid (ICF), total body water (TBW), and ECF as a percentage of TBW (ECF%TBW) were analyzed. ECF%TBW values for the HF and control populations differed significantly (49.2 ± 3.2% vs. 45.2 ± 2.1%, respectively; p < 0.001); both distributions satisfied criteria for normality. Interquartile ranges did not overlap (46.7-51.0% vs. 43.8-46.4%, respectively; p < 0.001). Subgroup analyses of HF patients who underwent transthoracic echocardiography showed that impedance measurements correlated with inferior vena cava size (Pearson correlation -0.73, p < 0.0001). A case study is presented for illustrative purposes. Conclusions: BIS-measured ECF%TBW values were significantly higher in HF patients as compared to adults without HF. We describe three strata of ECF%TBW (normal, elevated, fluid overload) that may aid in clinical risk stratification and fluid volume monitoring of HF patients. Clinical Trial Registration: COMPARE - www.ClinicalTrials.gov; IMPEL - www.ClinicalTrials.gov; Heart Failure at Home - www.ClinicalTrials.gov, identifier: NCT02939053; NCT02857231; NCT04013373.
Keywords: bioimpedance spectroscopy; case study; extracellular fluid; heart failure; total body water.
Copyright © 2021 Accardi, Matsubara, Gaw, Daleiden-Burns and Heywood.
Conflict of interest statement
AA, AD-B, and JH provide consultancy services to ImpediMed. BM and RG are employees of ImpediMed. As funder of this clinical research, ImpediMed provided no-cost access to bioimpedance spectroscopy devices for use in accordance with clinical trial protocols. ImpediMed also provided funding for clinical trial-related costs and third-party data management and biostatistical support.
Figures


References
Publication types
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

