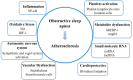
An Update on Obstructive Sleep Apnea for Atherosclerosis: Mechanism, Diagnosis, and Treatment
- PMID: 33898538
- PMCID: PMC8060459
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.647071
An Update on Obstructive Sleep Apnea for Atherosclerosis: Mechanism, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Abstract
The occurrence and development of atherosclerosis could be influenced by intermittent hypoxia. Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), characterized by intermittent hypoxia, is world-wide prevalence with increasing morbidity and mortality rates. Researches remain focused on the study of its mechanism and improvement of diagnosis and treatment. However, the underlying mechanism is complex, and the best practice for OSA diagnosis and treatment considering atherosclerosis and related cardiovascular diseases is still debatable. In this review, we provided an update on research in OSA in the last 5 years with regard to atherosclerosis. The processes of inflammation, oxidative stress, autonomic nervous system activation, vascular dysfunction, platelet activation, metabolite dysfunction, small molecule RNA regulation, and the cardioprotective occurrence was discussed. Additionally, improved diagnosis such as, the utilized of portable device, and treatment especially with inconsistent results in continuous positive airway pressure and mandibular advancement devices were illustrated in detail. Therefore, further fundamental and clinical research should be carried out for a better understanding the deep interaction between OSA and atherosclerosis, as well as the suggestion of newer diagnostic and treatment options.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; hypoxia; mechanism; obstructive sleep apnea; treatment.
Copyright © 2021 Chen, Lin and Zeng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Obstructive sleep apnea and atherosclerosis.Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2009 Mar-Apr;51(5):400-10. doi: 10.1016/j.pcad.2008.03.001. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2009. PMID: 19249446 Review.
-
Update on obstructive sleep apnea for neuro-ophthalmology.Curr Opin Neurol. 2019 Feb;32(1):124-130. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0000000000000630. Curr Opin Neurol. 2019. PMID: 30418196 Review.
-
Could the thromboxane A2 pathway be a therapeutic target for the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea-induced atherosclerosis?Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2015 Sep;121(Pt A):97-104. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2015.05.005. Epub 2015 May 28. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2015. PMID: 26026712 Review.
-
Roles and Mechanisms of Obstructive Sleep Apnea-Hypopnea Syndrome and Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia in Atherosclerosis: Evidence and Prospective.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:8215082. doi: 10.1155/2016/8215082. Epub 2016 May 16. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016. PMID: 27293515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurological Deficits in Obstructive Sleep Apnea.Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2017 Apr;19(4):16. doi: 10.1007/s11940-017-0451-8. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28374233 Review.
Cited by
-
A Potential Link between Myeloperoxidase Modified LDL, Atherosclerosis and Depression.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 13;25(16):8805. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168805. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201490 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Childhood asthma was associated with the presence of cardio-cerebrovascular diseases in US middle-aged and elderly.Prev Med Rep. 2024 May 9;43:102756. doi: 10.1016/j.pmedr.2024.102756. eCollection 2024 Jul. Prev Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 38826590 Free PMC article.
-
Ginsentide TP1 Protects Hypoxia-Induced Dysfunction and ER Stress-Linked Apoptosis.Cells. 2023 May 16;12(10):1401. doi: 10.3390/cells12101401. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37408235 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel biomarkers in obstructive sleep apnea via integrated bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation.PeerJ. 2023 Dec 4;11:e16608. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16608. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 38077447 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxic Regulation of the Large-Conductance, Calcium and Voltage-Activated Potassium Channel, BK.Front Physiol. 2021 Dec 22;12:780206. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.780206. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 35002762 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Roca GQ, Redline S, Claggett B, Bello N, Ballantyne CM, Solomon SD, et al. . Sex-specific association of sleep apnea severity with subclinical myocardial injury, ventricular hypertrophy, and heart failure risk in a community-dwelling cohort. Circulation. (2015) 132:1329–37. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.016985 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources