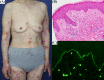
Bullous pemphigoid in a metastatic lung cancer patient associated with nivolumab
- PMID: 33898721
- PMCID: PMC8060659
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijwd.2020.09.001
Bullous pemphigoid in a metastatic lung cancer patient associated with nivolumab
Erratum in
-
Erratum regarding previously published articles.Int J Womens Dermatol. 2021 Sep 28;7(5Part B):868. doi: 10.1016/j.ijwd.2021.09.012. eCollection 2021 Dec. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 35028406 Free PMC article.
Keywords: Bullous pemphigoid; Lung cancer; Nivolumab; irAEs.
Figures
References
-
- Anastasopoulou A., Papaxoinis G., Diamantopoulos P., Christofidou E., Benopoulou O., Stratigos A. Bullous pemphigoid-like skin lesions and overt eosinophilia in a patient with melanoma treated with nivolumab: case report and review of the literature. J Immunother. 2018;41(3):164–167. - PubMed
-
- Hwang S.J.E., Carlos G., Chou S., Wakade D., Carlino M.S., Fernandez-Penas P. Bullous pemphigoid, an autoantibody-mediated disease, is a novel immune-related adverse event in patients treated with anti-programmed cell death 1 antibodies. Melanoma Res. 2016;26(4):413–416. - PubMed
-
- Jour G., Glitza I.C., Ellis R.M., Torres-Cabala C.A., Tetzlaff M.T., Li J.Y. Autoimmune dermatologic toxicities from immune checkpoint blockade with anti-PD-1 antibody therapy: a report on bullous skin eruptions. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43(8):688–696. - PubMed
-
- Lopez A.T., Khanna T., Antonov N., Audrey-Bayan C., Geskin L. A review of bullous pemphigoid associated with PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57(6):664–669. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

