Omega-3 effects on electrocorticographic patterns of adult Wistar rats exposed to ionizing radiation
- PMID: 33898765
- PMCID: PMC8056338
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2021.100992
Omega-3 effects on electrocorticographic patterns of adult Wistar rats exposed to ionizing radiation
Abstract
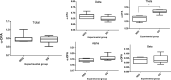
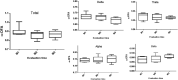
This study aimed to assess the effect of supplementation with omega-3 in Wistar rats exposed to ionizing radiation in a dose of 18 Gy on the cortical electrical activity, using mathematical methods such as the power spectrum (PS) and the detrended fluctuation analysis (DFA) in the evaluation of the electrocorticogram (ECoG) record. The PS analysis showed that in non-irradiated animals but supplemented with omega-3 there was a decrease in the power of the beta rhythm, while the DFA applied to different frequency ranges of the ECoG showed a significant increase in the long-range correlation only for the theta wave when compared with non-supplemented animals. In the evaluation of the radiation effect through the PS, an increase in the power of the theta rhythm was observed in both groups (non-supplemented and supplemented animals) only when they were evaluated one week after irradiation. The DFA method also showed difference in this wave. The PS and DFA methods applied to the ECoG record allowed a quantitative analysis of the cortical electrical activity in rats in response to the omega-3 effects, ionizing radiation, or both.
Keywords: Brain electrical activity; Head–neck irradiation; Polyunsaturated fatty acid.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Long-term correlation of the electrocorticogram as a bioindicator of brain exposure to ionizing radiation.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2015 Oct;48(10):915-22. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20154473. Epub 2015 Jun 12. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2015. PMID: 26445335 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of diet with omega-3 in basal brain electrical activity and during status epilepticus in rats.Epilepsy Res. 2017 Nov;137:33-38. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2017.08.014. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Epilepsy Res. 2017. PMID: 28892741
-
Analysis of electrocorticographic patterns in rats fed standard or hyperlipidic diets in a normal state or during status epilepticus.Nutr Neurosci. 2016 Jun;19(5):206-12. doi: 10.1179/1476830515Y.0000000033. Epub 2015 Jun 16. Nutr Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26076770
-
Live-cell imaging to detect phosphatidylserine externalization in brain endothelial cells exposed to ionizing radiation: implications for the treatment of brain arteriovenous malformations.J Neurosurg. 2016 Jun;124(6):1780-7. doi: 10.3171/2015.4.JNS142129. Epub 2015 Oct 2. J Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 26430846
-
Cerebral impact of prenatal irradiation by 131I: an experimental model of clinical neuroradioembryological effects.Probl Radiac Med Radiobiol. 2017 Dec;22:238-269. Probl Radiac Med Radiobiol. 2017. PMID: 29286511 English, Ukrainian.
Cited by
-
X-ray perception: Animal studies of sensory and behavioral responses to X-rays.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Aug 2;16:917273. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.917273. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36052341 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sharma N.K., Sharma R., Mathur D., Sharad S., Minhas G., Bhatia K., Anand A., Gosh S.P. Role of ionizing radiation in neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018;v10 https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fnagi.2018.00134 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mahan L.K., Escott-Stump S., Raymond J.L., Alimentos . nutrição e dietoterapia. thirteenth ed. Saunders-Elsevier; Rio de Janeiro: 2010.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

